Explain carbon and oxygen aspect of using phase rule?
Consider a system containing solid carbon (graphite) and a gaseous mixture of O2, CO, and CO2. There are four species and two phases. If reaction equilibrium is absent, as might be the case at low temperature in the absence of a catalyst, we have r = 0 and C = s - r = 4. The four components are the four substances. The phase rule tells us the system has four degrees of freedom. We could, for instance, arbitrarily vary T, p, yO2, and yCO. Now suppose we raise the temperature or introduce an appropriate catalyst to allow the following reaction equilibria to exist:
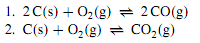
These equilibria introduce two new independent relations among chemical potentials and among activities. We could also consider the equilibrium 2 CO (g) + O2 (g) ↔2CO2 (g), but it does not contribute an additional independent relation because it depends on the other two equilibria: the reaction equation is obtained by subtracting the reaction equation for equilibrium 1 from twice the reaction equation for equilibrium 2. By the species approach, we have s = 4, r = 2, and P = 2; the number of degrees of freedom from these values is
F = 2 + s - r - P = 2
If we wish to calculate F by the components approach, we must decide on the mini- mum number of substances we could use to prepare each phase separately. (This does not refer to how we actually prepare the two-phase system, but to a hypothetical preparation of each phase with any of the compositions that can actually exist in the equilibrium system.) Assume equilibria 1 and 2 are present. We prepare the solid phase with carbon, and we can prepare any possible equilibrium composition of the gas phase from carbon and O2 by using the reactions of both equilibria. Thus, there are two components (C and O2) giving the same result of two degrees of freedom. What is the significance of there being two degrees of freedom when the reaction equilibria are present? There are two ways of viewing the situation:
1. We can arbitrarily vary the two intensive variables T and p. When we do, the mole fractions of the three substances in the gas phase change in a way determined by equilibria 1 and 2.
2. If we specify arbitrary values of T and p, each of the mole fractions has only one possible value that will allow the two phases and four substances to be in equilibrium.
Now to introduce an additional complexity: Suppose we prepare the system by placing a certain amount of O2 and twice this amount of carbon in an evacuated container, and wait for the reactions to come to equilibrium. This method of preparation imposes an initial condition on the system, and we must decide whether the number of degrees of freedom is affected. Equating the total amount of carbon atoms to the total amount of oxygen atoms in the equilibrated system gives the relation
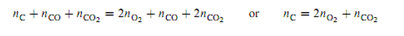
Either equation is a relation among extensive variables of the two phases. From them, we are unable to obtain any relation among intensive variables of the phases. Therefore, this particular initial condition does not change the value of r, and F remains equal to 2.