Explain An Overview of Water Soluble Vitamins?
Vitamins, we already know, are classified by the materials in which they will dissolve. Fat-soluble vitamins -vitamin A, D, E and K- about which we learnt in the last Unit, dissolve in fat before they are absorbed in the blood stream to carry out their functions. Excesses of this vitamin are stored in the liver. Because they are stored, they are not needed every day in the diet. By contrast, water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water and are not stored. They are eliminated in urine. We need a continuous supply of them in our diets. The water-soluble vitamins are the B-complex group and vitamin C.
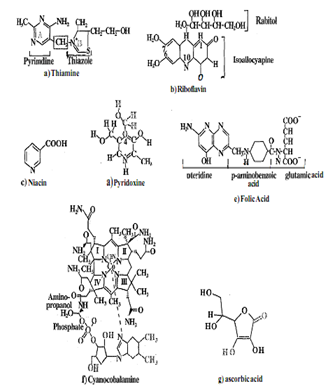
Vitamin B-complex, as the name suggests, comprises of a group of vitamins which essentially are same in many respects, However, in this unit, we shall focus on six of these- thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, pyridoxin, folic acid and cynacobalamin - which along with other B-complex vitamins are considered to be essential from nutrition point of view. All water-soluble vitamins have cyclic sing structures with side chains and are alcohols, amines or acids. All of them are enzymes, coenzymes or apoenzymes and have key roles in several metabolic reactions. Vitamin C or ascorbic acid, on the other hand, is a compound that is structurally similar Lo carbohydrate and plays important physiological roles. Being water-soluble, the B-complex and C vitamins are readily absorbed from the different regions of the small intestine. Water-soluble vitamins are easily destroyed or washed out during food storage or Preparation Proper storage and preparation of food can minimize vitamin loss.
Clinical manifestations of deficiency of some B vitamins- such as beriberi (cardiac and dry), peripheral neuropathies, pellagra, and oral and genital lesions (related Lo riboflavin deficiency) -were once major public health problems in some parts of the world. These manifestations have now declined, the decline being brought about through changes in the patterns of food availability and consequent changes in dietary practices. Although many clinical manifestations of B-vitamin deficiencies have decreased, there is evidence of widespread subclinical deficiency of these vitamins (especially of riboflavin and pyridoxin). These subclinical deficiencies, although less dramatic in their manifestations, exert deleterious metabolic effects.In our discussion in this unit, we shall focus on the food sources, the mechanism of absorption, storage and elimination, important physiological roles, deficiency diseases and the concept of bioavailability for each of these vitamins.