There are two periods. You observe that Jack consumes 100 apples in period t = 0, and 120 apples in period t = 1. That is,
(c0; c1) = (100; 120)
Suppose Jack has the utility function:
U(c0; c1) = u(c0) + u (c1)
where the felicity function u has the power form. Notice that Jack does not discount the future.
Savings carry 1 percent interest.
(i) Assume that Jack did not face any borrowing constraints when making his choice. What is the � that is consistent with Jack's chosen consumption pro�le?
(ii) Assume now that Jack could not borrow as much as he wanted when he chose the above consumption allocation. Draw a graph that depicts this scenario. Derive a lower bound for Jack's �.
(iii) Relate your answers to the risk-free rate puzzle.
Problem:
Consider the following utility function for money:
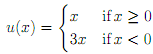
Consider the Samuelson gamble in which with equal probability you win $200 or lose $100.
(i) Show that an expected-utility maximizer with the above utility function u(x) will turn down a single play of the gamble, but will accept three such gambles.
(ii) if you are ambitious..., is any n-fold repetition accepted, where n � 3?
(iii) How does this problem relate to Samuelson's claim that accepting a large number of IID gambles while rejecting a single one is a 'fallacy of large numbers'?
Problem
Benartzi and Thaler recount the following experience. When consulting a large investment company, they confronted each fund manager with a simple gamble. The majority of the fund managers rejected the gamble. The CEO of the company noted that he would prefer if all the managers had accepted their gamble. How does this anecdote relate to Samuelson's IID paradox and his discussion of the fallacy of large numbers?
Problem
An expected-utility maximizer whose utility for money is increasing is indifferent between $40 and the lottery (1=2; 0; 1=2; 100). He is also indi�erent between $105 and the lottery (1=2; 0; 1=2; 220). Is the individual risk-averse?
Problem An asset pays $5 in state !1 and $2 in state !2. A 'maxmin' investor believes that the probability of state !1 lies in the interval [1=3; 2=3].
(i) What is the highest price at which the investor will be willing to buy the asset?
(ii) What is the minimal price at which the investor will be willing to short sell the asset?
(iii) For what range of prices does the investor stay out of the market?
Problem
Jack uses the following utility-function when making consumption-savings decisions under uncertainty:
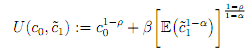
(i) How should the parameter � be interpreted?
(ii) How should the parameter � be interpreted?
(iii) Suppose we use the above utility speci�cation to address the equity premium puzzle. What values for �α, p� do you expect to fi�nd?