Suppose that in an organisation, an employee may do different roles in dissimilar projects. Say, RAM is doing coding in one project and doing designing in another. Suppose that the information is set by the organisation in 3 different relations named EMPLOYEE, PROJECT and ROLE. The ROLE relation tells the different roles needed in any project.
Suppose that the relational schema for the above 3 relations are:
EMPLOYEE (EMPID, Name, Designation)
PROJECT (PROJID, Proj_Name, Details)
ROLE (ROLEID, Role_description)
In the relations over EMPID, PROJID and ROLEID are not NULL and unique, respectively. As we can clearly see, we can recognize the complete instance of the entity set employee by the attribute EMPID. Thus EMPID is the primary key of the relation EMPLOYEE. Likewise PROJID and ROLEID are the primary keys for the relations PROJECT and ROLE respectively.
Let ASSIGNMENT is a relationship among entities EMPLOYEE and PROJECT
and ROLE, Explain which employee is working on which project and what the
role of the employee is in the given project. Figure shows the E-R diagram for these entities and relationships.
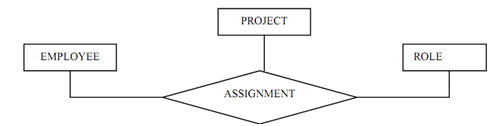
Figure: E-R diagram for employee role in development team
Let us consider sample relation instances as
PROJECT
|
PROJID
|
Proj_name
|
Details
|
|
TCS
|
Traffic Control
System
|
For traffic
shaping.
|
|
LG
|
Load Generator
|
To simulate load
for input in TCS.
|
|
B++1
|
B++_TREE
|
ISS/R turbo sys
|
|
|
EMPLOYEE
|
EMPID
|
Name
|
Designation
|
|
101
|
RAM
|
Analyst
|
|
102
|
SITA
|
Receptionist
|
|
103
|
ARVIND
|
Manager
|
ASSIGNMENT
|
ROLEID
|
Role_descrption
|
|
1000
|
Design
|
|
2000
|
Coding
|
|
3000
|
Marketing
|
|
|
|
Role
|
PROJID
|
Proj_name
|
Details
|
|
101
|
TCS
|
1000
|
|
101
|
LG
|
2000
|
|
102
|
B++1
|
3000
|
|
We can describe the relational scheme for the relation ASSIGNMENT as follows: ASSIGNMENT (EMPID, PROJID, and ROLEID)
Please note down now that in the relation ASSIGNMENT (as per the definition to be taken as R2) EMPID is the foreign key in ASSIGNMENT relation; it references the relation EMPLOYEE (as per the definition to be taken as R1) where EMPID is the primary key. Likewise ROLEID and PROJID in the relation ASSIGNMENT are foreign keys referencing the relation ROLE and PROJECT respectively.
Now after defining the theory of foreign key, we can proceed to talk about the real integrity constraints namely Entity Integrity and Referential Integrity.