Discontinuous Integrand- Integration Techniques
Here now we need to look at the second type of improper integrals that we will be looking at in this section. These are integrals which have discontinuous integrands. The procedure here is mainly the same with one subtle variation. Here are the common cases that we'll look at for these integrals.
1. If f (x) is continuous on the interval [a, b] and not continuous at x = b then,
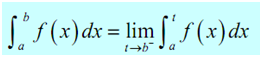
specified the limit exists and is finite. Note also that we do need to make use of a left hand limit here as the interval of integration is completely on the left side of the upper limit.
2. Determine If f (x) is continuous on the interval (a, b) and not continuous at x = a then,
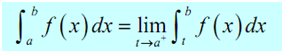
specified the limit exists and is finite. In this case we need to make use of a right hand limit here as the interval of integration is completely on the right side of the lower limit.
3. If f (x) is not continuous at x = c where a < c < b and ∫ca f(x) dx and ∫bc f(x) dx are both convergent then,
∫ ba f (x) dx
= ∫ ca f(x) dx + ∫ bc f(x) dx
Since with the infinite interval case this needs BOTH of the integrals to be convergent in order for this integral to as well are convergent. Determine if either of the two integrals is divergent then so is this integral.
4. If f (x) is not continuous at x = a and x = b and if ∫ca f(x) dx and ∫bc f(x) dx are both convergent then
∫ ba f(x) dx = ∫ca f(x) dx + ∫bc f (x) dx
In which c is any number, once Again this needs BOTH of the integrals to be convergent in order for this integral to as well be convergent.