Derivation of Indifference Curve:
Consider any commodity bundle denoted by point A in the above figure which consist x01 and x02 amount of good I and good II respectively and from which consumer obtains particular level of utility, say U0. We compare the commodity bundle 'A' with other commodity bundle in the commodity space. For that we divide the entire commodity plane into four phases from 'A'. Consider any point in phase I say β, where we have large quantity of both x1 and x2 compared to point 'A'. Again, if we consider any point say 'a' in horizontal line in phase I, we have larger quantity of x1 with same quantity of x2 compared to point 'A'. Similarly, for any point 'b' in vertical axis, we have larger x2 with same x1. That means in phase I including the borderlines, we have larger quantity of at least one commodity and no less quantity of any other commodity compared to 'A'. Thus, we have larger utility in phase I including the borderlines compared to 'A'.
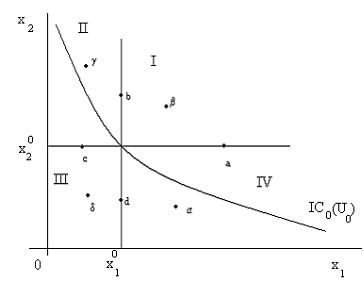
By similar logic, we have lower consumption of at least one good and no larger consumption of any other good in phase III including the borderlines compared to point 'A'. Hence, we have lower level of utility in phase III including the borderlines compared to 'A' by the axiom of non-satiation for all goods.
Clearly, in phases I and III, including borderlines, utility is not constant between the commodity bundles compared to point 'A'. So, indifference curve (along which utility is constant) can't pass through phases I and III including their borderlines.
Consider any point in phase IV excluding borderlines, say α. We have larger x1 (for which utility is larger) and lower x2 (for which utility is lower) compared to 'A'. Since both goods are non-satiated, utility of point α may be larger, lower or equal compared to point 'A'. Similarly, for any point in phase II excluding the borderlines, say δ, we have larger consumption of x2 but lower of x1 compared to point 'A'. Therefore, by axiom of non-satiation in all goods, utility at point δ may be larger, lower or equal compared to 'A'.
Clearly, only in phases II and IV excluding the borderlines, there is a possibility of the same level of utility between the bundles compared to point 'A'. So, indifference curve, along which utility remains unchanged, must pass through the phase II and phase IV, excluding their lines. Thus, indifference curve is necessarily downward sloping where all goods are non-satiated given that a consumer choice is continuous, reflexive and complete.