Deletion Anomalies: Loss of important Information: In some cases, useful information may be lost when a tuple is deleted. For instance, if we delete the tuple corresponding to student 050111341 enrolled for MCS-014, we will misplace relevant information about the student by enrolment number, address and name of this student. Likewise deletion of tuple having Sname "Rahul" and Cno 'MCS-012" will result in failure of information that MCS-012 is named computer organisation having an instructor "Anurag Sharma", whose office number is 105. This is known as deletion anomaly.
The anomalies arise primarily as the relation STUDENT has information about students as well as subjects. One solution to the troubles is to decompose the relation into two or more smaller relations. But what should be the basis of this decomposition? To solution the questions let us attempt to formulate how data is related in the relation with the help of the following Figure:
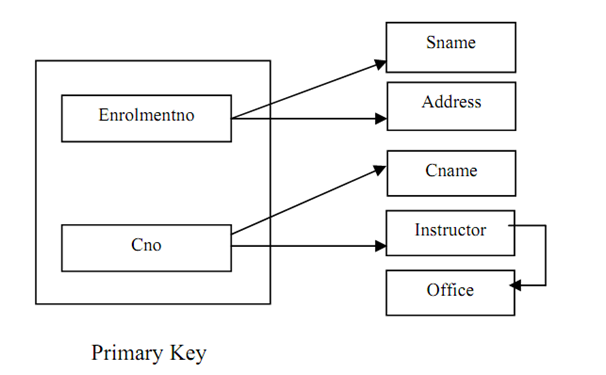
Figure : The dependencies of relation
Please note that the arrows in Figure are defines data inter-relationship. For instance, enrolment no column is unique for a student so if we identify the enrolment no of a student we can uniquely describe his/her name and address. Likewise, the course code (Cno) uniquely defines course name (Cname) and Instructor (we are assuming that a course is taught by only single instructor). Please also note one vital interrelationship in Figure that is, the Office (address) of an instructor is relying on Instructor (name), assuming unique instructor names. The root cause of the being there of anomalies in a relation is determination of data by the components of the non-key and key attributes.
Normalisation includes decomposition of a relation into minor relations based on the concept of functional dependence to come over undesirable anomalies.
Normalisation few times can affect performance. As it results in decomposition of tables, few queries desire to join these tables to create the data once again. But such performance overheads are smallest as Normalisation results in minimisation of data redundancy and may result in minor relation sizes. Also DBMSs executes optimised algorithms for joining of relations and many indexing schemes that decrease the load on joining of relations. In any case the benefits of normalization normally overweigh the performance constraints. Normalisation does lead to more well-organized updates since an update that might have needs various tuples to be updated, while normalised relations, in general, need the information updating at only one place.
A relation that requires to be normalised may have a very large number of attributes. In such relations, it is almost impossible for someone to conceptualise all the information and recommend a suitable decomposition to overcome the troubles. Such relations require an algorithmic approach of searching if there are troubles in a proposed database design and how to remove them if they exist. The discussions of these algorithms are beyond the scope of this part, except, we will initial introduce you to the basic concept that supports the process of Normalisation of big databases. So let us first describes the concept of functional dependence in the subsequent part and follow it up with the thoughts of normalisation.