Define Cercaria Larva?
Cercaria larva is the fourth larval stage in the life-cycle of F, hepatica. It is a free living stage produced by the redia larva.
1. It has a flat and oval body about 35 mm in length and a long tadpole like tail.
2. Cercaria moves by muscular undulations of the tail.
3. Cercaria has two suckers an anterior, oral sucker surrounding the mouth and a ventral sucker situated in the middle of the body.
4. Body space is filled with parenchyma and contains a few cystogenous glands on each side which form tile cyst of the future larva.
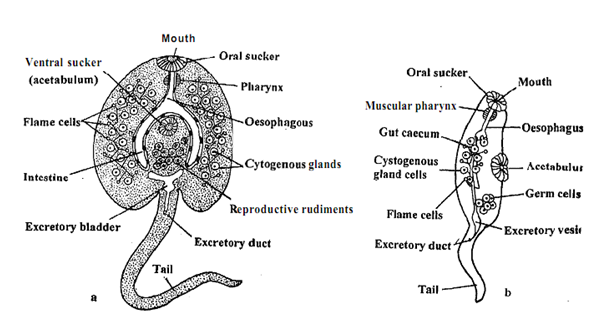
5. The alimentary canal consists of mouth, muscular pharynx, oesophagus and bifurcated and inverted Y-shaped intestine.
6. It also possesses an excretory bladder with a pair of protonephridial canals and a number of flame cells.
7. Cercaria also has two large non-functional penetration glands as well as rudiments of reproductive organs which have originated from germ cells.
8. Cercaria is a young fluke of sexual generation.
9. Cercaria larva first comes out of the redia through its birth pore and then also from the bogy of its snail host.