Data Distribution
Data distribution directives tell the compiler how the program data is to be distributed between the memory areas associated with a set of processors. The logic used for data distribution is that if a set of data has independent sub-blocks, then computation on them can be carried out in parallel. They do not let the programmer to state directly which processor will do a particular computation. But it is expected that if the operands of a particular sub-computation are all found on the similar processor, the compiler will allocate that part of the computation to the processor holding the operands, where upon no remote memory accesses will be include.
Having seen how to describe one or more target processor arrangements, we need to introduce mechanisms for distributing the data arrays above those arrangements. The DISTRIBUTE directive is used to supply a data object) onto an abstract processor array.
The syntax of a DISTRIBUTE directive is:
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE array_lists [ONTO arrayp]
Where array_list is the list of array to be distributed and arrayp is abstract processor array. The ONTO specifier can be used to do a distribution across a particular processor array. If no processor array is showing, one is chosen by the compiler.
HPF allows arrays to be distributed over the processors directly, but it is often more convenient to go through the intermediary of an explicit template. A template can be declared in much the similar way as a processor arrangement.
!HPF$ TEMPLATE T(50, 50, 50)
declares a 50 by 50 by 50 three-dimensional template called T. Having declared it, we can create a relation between a template and some processor arrangement by using DISTRIBUTE directive. There are three methods in which a template may be distributed over Processors: Block, cyclic and *.
(a) Block Distribution
Simple block distribution is identified by
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE T1(BLOCK) ONTO P1
where T1 is some template and P1 is some processor arrangement.
In this case, every processor gets a contiguous block of template elements. All processors get the similar sized block. The last processor may get lesser sized block.
Example 3:
!HPF$ PROCESSORS P1(4)
!HPF$ TEMPLATE T1(18)
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE T1(BLOCK) ONTO P1
As a result of these instructions, distribution of data will be as shown in Figure.
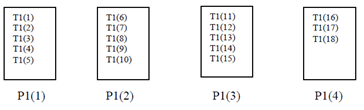
Block Distribution of Data
In a variant of the block distribution, the number of template elements allocated to every processor can be explicitly identified, as in
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE T1 (BLOCK (6)) ONTO P1
Distribution of data will be as shown in Figure.
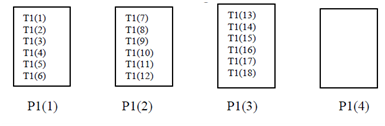
Variation of Block Distribution
It means that we allocate all template elements earlier than exhausting processors, some processors are left empty.
(b) Cyclic Distribution
Simple cyclic distribution is specified by
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE T1(CYCLIC) ONTO P1
The first processor gets the first template element, the second gets the second, and so on. When the set of processors is exhausted, then go back to the first processor, and continue allocating the template elements from there.
Example 4
!HPF$ PROCESSORS P1(4)
!HPF$ TEMPLATE T1(18)
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE T1(CYCLIC) ONTO P1
The result of these instructions is shown in Figure .
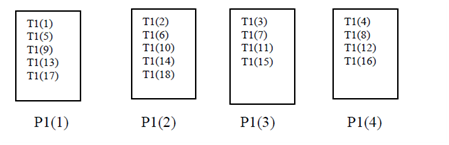
Cyclic Distribution
But in an analogous variant of the cyclic distribution
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE T1 (BLOCK (3)) ONTO P1
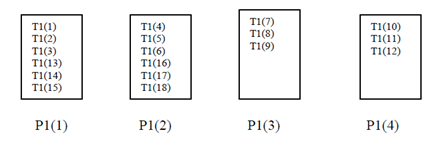
Variation of Cyclic Distribution
That covers the case where both the processor and the template are one dimensional. When the and processor have (the same) higher dimension, each dimension can be distributed independently, mixing any of the four distribution formats. The correspondence among the template and the processor dimension is the obvious one. In
!HPF$ PROCESSORS P2 (4, 3)
!HPF$ TEMPLATE T2 (17, 20)
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE T2 (CYCLIC, BLOCK) ONTO P2
the first dimension of T2 is distributed cyclically over the first dimension of P2; the second dimension is distributed blockwise over the second dimension of P2.
(c) * Distribution
Some dimensions of a template might have ''collapsed distributions'', allowing a template to be distributed onto a processor arrangement with fewer dimensions than the template.
Example 5
!HPF$ PROCESSORS P2 (4, 3)
!HPF$ TEMPLATE T2 (17, 20)
!HPF$ DISTRIBUTE T2 (BLOCK, *) ONTO P1
means that the first dimension of T2 will be distributed over P1 in blockwise order but for a fixed value of the first index of T2, all values of the second subscript are mapped to the same processor.