Q. Complexation Behaviour of Group 13?
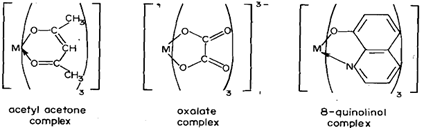
As compared to the elements of Groups 1 and 2, elements of Group 13 show a greater tendency of complex formation. Because of lack of d-orbitals, boron is invariably tetrahedrallv coordinated in these compounds. For example, in compounds like NaBH4, NaBF4, NaB(C6H5,)4 BH3.NMe3, BF3-NH3 as well as in chelates such as [B(O-C6H4,O2)2]- and [B(o-OC6H,CO4)2]- the coordination number of boron atom is four. Due to the presence of d-orbitals, the higher members of the group can expand their coordination number even up to six. Thus, Al, Ga, In and T1 form complexes such as (i) AlCl3.NMe3, RCO+AIX4(X= CI, Br), Et4N+MX4 (M = Al, Ga,X=Cl, Br) in which the coordination number is four, (ii) AlCl3.2NMe3, in which the coordination number is five, and (iii) Na3[AlF6] in which the coordination number is six. With chelating ligands like p-dike tones, pyrocatechol, dicarboxylic acids and 8-quinolinol, Al, Ga, In and T1 form anionic or neutral complexes in which the coordination number of the metal is six. Structures of some of these complexes are shown in Fig. 6.10.
You know that the formation of AlCl-4, is important in Friedel-Crafts reaction whereas the 8-quinolinol complex of aluminium is used in gravimetric estimation of aluminium.
In addition to coordination complexes, aluminium forms a number of double sulphates of general formula MAI (S04)2.12H20, where M is usually K, Rb, Cs or NH4. These double sulphates are known as alums. For example, potash alum, KAl (S04)2.12H20 and ammonium alum, NH4AI (S04)2.12H20 In alums, A1 can- .also be replaced by a number of cations of the same charge and not too different in size, e.g., Ga, In, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe and Co. For example, chrome alum, KCr(S04)2.12H20 and ferric alum, NH4Fe(S04)2.12H20. The alums are isomorphism with each other. It is important to realise that the alums are double salts and not complex salts. In solution they behave simply as a mixture of component sulphates and give reactions of their individual cations.