We will be looking at solutions to the differential equation, in this section
ay′′ + by′ + cy = 0
Wherein roots of the characteristic equation,
ar2 + br + c = 0
Those are complicated roots in the form,
r12 = λ + µi
Here, recall that we arrived at the characteristic equation through assuming that each solution to the differential equation will be of the type
y (t ) = ert
Plugging our two roots in the general form of the solution provides the subsequent solutions to the differential equation.
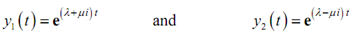
Here, these two functions are "nice enough" for the form the general solution. We do have a problem though. As we started along with only real numbers in our differential equation we would like our solution to only include real numbers. The two solutions above are complicated and thus we would like to find our hands on a couple of solutions as "nice enough" obviously, which are real.
To do this we will require Euler's Formula.
eiq = cosq+ i sinq
A nice variant of Euler's Formula which we'll want is,
eiq = cos(-q) + i sin(-q) = cosq - i sin q
Currently, split up our two solutions into exponentials which only have real exponents and then exponentials which only have imaginary exponents. After that use Euler's formula, or its variant use to rewrite the second exponential as:
y1(t) = elt eiµt = elt (cos(µ t)) + i sin (µt))
Y2(t) = elt e-iµt = elt (cos(µ t)) - i sin (µt))
This doesn't remove the complex nature of the solutions, although this does put the two solutions in a form that we can remove the complex parts.
Recall from the fundamentals section which if two solutions are "nice enough" so any solution can be written like a combination of the two solutions. Convertselyu,
y (t ) = c1 y1 (t ) + c2 y2 (t) will also be a solution.
By using this let's see that if we add the two solutions together we will attain.
y1(t) + Y2(t) = 2elt cos(µ t)
It is a real solution and just to remove the extraneous 2 let's divide everything through a 2. It gives the first real solution which we're after.
µ (t) = ½ y1(t) + ½ y2 (t) = elt cos(µ t)
Notice there that this is just equal to taking
c1 = c2 = ½
Here, we can reach a second solution in a same manner. Here we subtract the two original solutions to find out.
y1(t) - Y2(t) = 2ielt sin(µ t)
On the surface which doesn't show to fix the problem as the solution is until now complex. Though, upon learning that the two constants, c1 and c2 can be complex numbers so we can reach a real solution by dividing this through 2i. It is equal to taking,
c1 = 1/2i, c2 = -(1/2i)
Our second solution will after that be,
n (t) = (1/2i) y1(t) - ((1/2i) y2(t)) = elt sin (µt)
We here have two solutions as we'll leave this to you to verify that they are actually solutions to the differential equation.
µ(t) = elt cos (µt), and n (t) = elt sin (µt)
This also turns out that these two solutions are "nice enough" to make a general solution.
Thus, if the roots of the characteristic equation occur to be, r12 = l+mI the differential equation is,
y(t) = c1 elt cos (µt)+ c elt sin (µt)