BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF PROTOPLASM -
1. Respiration - Oxidation of food to liberate energy is respiration. Every living beings respire but every living beings do not breathe.
2. Excretion - After oxidation of food to give out nitrogenous waste products is known as excretion
3. Metabolism - Word given by Shwann. It is constructive as well as destructive process Constructive process is Anabolism. Destructive process is Catabolism
4. Irritability - Response against external stimuli is known as Irritability. Also known as taxis or topotaxis. It may be phillotaxis or phobotaxis.
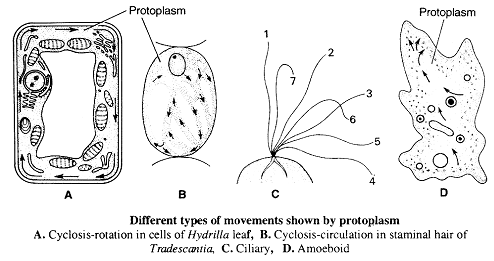
5. Movement -
(i) Cyclosis - Movement of cytoplasm is known as cyclosis.
Cyclosis is of 2 types -
(a) Rotation - Protoplasm move around a vacuole inside a cell in one direction only (Clockwise/Anticlockwise) e.g. leaf cells of Hydrilla or Vallisaneria It is unidirectional
(b) Circulation - Protoplasm moves in different directions around different small vacuoles inside a cell. It may be clockwise and anticlockwise. It is bidirectional, e.g. staminal hair of Tradescantia plant.
(ii) Brownian movement - Colloid particles have electric charge and due to charges these remains in a continuous random motion called Brownian movement. Brownian movement and cyclosis are more significant in sol stage.
(iii) Ciliary movement- When an organism as a whole or zoospores or gametes move from one place to another with the help of cilia then this motion is called ciliary movement. e.g. Chlamydomonas, Zoospores of Ulothrix Albugo.
(iv) Amoeboid movement - Protoplasm moves with the help of pseudopodia. e.g. Sarcodina, Slime mould.