ARINC 429 DATA Bus SPECIFICATIONS:
ARINC 429 sets specifications for the transfer of digital data between aircraft electronic system components and is a "One-way" communication link between a single transmitter and multiple receivers. ARINC 429 system provides for the transmission of up to 32 bits of data. One of three languages must be used to conform to the ARINC 429 standards:
1. Binary.
2. Binary Coded Decimal (BCD).
3. Discrete.
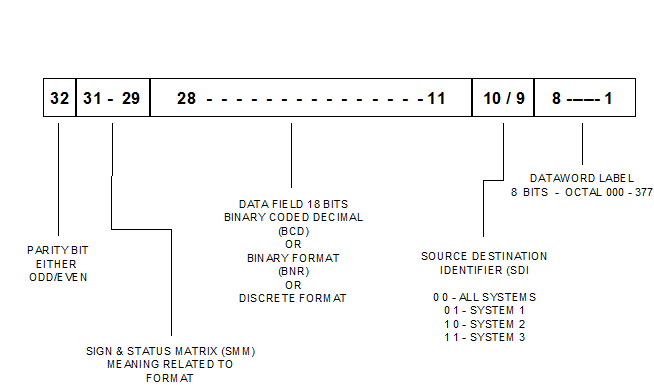
ARINC 429 assigns the first 8 bits as the word label; bits 9 and 10 are the "Source-Destination Indicator" (SDI), bits 11 through to 28 provide data information; bits 29 through to 31 are the "Sign-Status Matrix" (SSM), and bit 32 is a "Parity Bit.
There are 256 combinations of word label in the ARINC 429 code. Each word is coded in an octal notation language and is written in reverse order. The source-destination indicator serves as the address of the 32-bit word. That is, the SDI identifies the source or destination of the word. All information sent to a common serial bus is received by any receiver connected to that bus. Each receiver accepts only that information labelled with its particular address; the receiver ignores all other information.
The information data of an ARINC 429 coded transmission must be contained within the bus numbered 11 through to 28. This data is the actual message that is to be transmitted. For example, a Digital Air Data Computer (DADC) may transmit the binary message 0110101001 for Indicated Airspeed. Translated into decimal form, this means 425, or an airspeed of 425 knots. The sign-status matrix provides information that might be common to several peripherals (plus or minus, north or south, right or left etc). The parity bit of ARINC 429 code is included to permit error checking by the ARINC receiver. The receiver also performs a "Reasonableness Check", which deletes any unreasonable information. This ensures that if a momentary defect occurs in the transmission system resulting in unreasonable data, the receiver will ignore that signal and wait for the next transmission.
The parity bit will either be set to 1 or 0 depending on the parity used. The parity used in ARINC 429 is "Odd Parity". If there is an even number of 1 bits in a transmitted word (bits 1 through 31), the parity bit must be 1 to ensure the whole word contains an odd number of 1 bits in the word.