3-D Transformation
The capability to represent or display a three-dimensional object is basically to the knowing of the shape of that object. Moreover, the capability to rotate, translate and also project views of such object is also, in various cases, basically to the understanding of its shape. Manipulation, construction and viewing of 3-dimensional graphic images need the utilization of coordinate transformations and 3-dimensional geometric. Within geometric transformation, the coordinate system is set and the desired transformation of the object is finished w.r.t. the coordinate system. During coordinate transformation, the object is fixed and the preferred transformation of the object is complete on the coordinate system itself. Such transformations are formed via composing the essential transformations of translation, rotation and scaling. All of these transformations can be demonstrated as a matrix transformation. It permits more complex transformations to be constructed by utilization of matrix concatenation or multiplication. We can make the complicated objects/pictures, via immediate transformations. In order to demonstrate all these transformations, we require utilizing homogeneous coordinates.
Thus, if P(x,y,z) be any point in 3-dimensional space then in Homogeneous coordinate system, we add a fourth-coordinate to a point. It is in place of (x,y,z), all points can be represented via a Quadruple (x,y,z,H), where H≠0; along with the condition is x1/H1=x2/H2; y1/H1=y2/H2; z1/H1=z2/H2. For two points (x1, y1, z1, H1) = (x2, y2, z2, H2) ; such that H1 ≠ 0, H2 ≠ 0. Hence any point (x,y,z) in Cartesian system can be illustrated by a four-dimensional vector like (x,y,z,1) in HCS. Similarly, if (x,y,z,H) be any point in Homogeneous coordinate system then (x/H,y/H,z/H) be the equivalent point in Cartesian system. Hence, a point in 3-dimensional space (x,y,z) can be demonstrated by a four-dimensional point as: (x',y',z',1)=(x,y,z,1).[T], here [T] is several transformation matrix and (x',y'z',1) is a new coordinate of a specified point (x,y,z,1), so after the transformation.
The completed 4x4 transformation matrix for 3-dimensional homogeneous coordinates as:
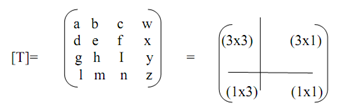
The upper left (3x3) sub matrix generates scaling, reflection, rotation and shearing transformation. The lower left (1x3) sub-matrix generates translation and the upper right (3x1) sub-matrix produces a perspective transformation that we will study in the subsequent section. The final lower right-hand (1x1) sub-matrix generates overall scaling.