Reference no: EM131235209
Telecommunications System Modelling
You are responsible for the planning of roads in a small suburb shown in Figure below. There are 4 intersections, labelled 1 to 4. The outside of this suburb has been represented by areas 0 and 5. Each street segment is named based on the two intersections that it connects to in the direction of traffic flow. For example, s12 is the road segment connecting intersection 1 to intersection 2. The opposite direction would be called s21.
Similarly, s01 connects the left-hand outside area 0 to intersection 1, and s35 connects the intersection 3 to the outside area 5 at the bottom. Some example names for streets are shown on the figure.
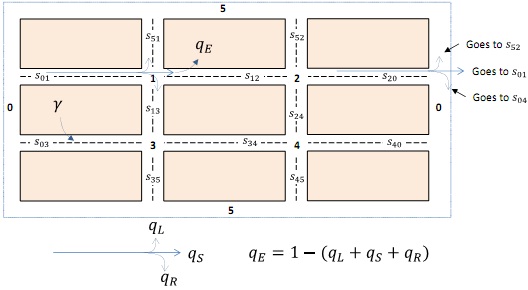
When cars arrive at an intersection, a percentage qL of them turn left, qR turn right, and qS go straight. Also, a percentage qE will leave the street network (going home or to their office). These percentages are the same for all intersections. At the edge of the suburb, the turning cars will re-enter the suburb at the next available street and the ones going straight are recycled back from the other end as shown in the Figure. This is meant to model arrivals from other neighbouring suburbs to this area.
The cars arrive to the system (from houses or offices) at a rate of ?? in each street segment (same rate for all segments) according to a Poisson process.
To model the queue at the intersection, you can use an M/M/k queue, where k is the number of lanes in the street. The cars depart the intersection at the rate of μ cars per second for each lane. In other words, μ is the service rate of each lane (each lane is a server in the terminology of queueing theory). If k > 1 in any intersection, it means that cars have more than one lane so this becomes a multi-server queue. Of course, making streets wider to have more than one lane is very costly, so the aim is to identify the minimum number of lanes that are sufficient to give a reasonable congestion delay for the commuters. Your tasks are as follows:
1- Model this street network as a Jackson queuing network. Identify all relevant parameters of the system.
2- Write down the expressions for the total average delay (W) in the system, as well as other relevant indicators such as the size of queues at intersections. Clearly state any assumptions that you have to make.
3- Discuss how W is related to k. It is expected that as k increases, then the congestion delay is reduced. Is this correct?
4- Solve this problem and obtain W (if a steady state solution exists) for the following numerical example: γ = 2, μ = 8, qL = qR = 0.2, qS = 0.4, qE = 0.2, k = 2. Use Matlab for this purpose and attach your code. Discuss the solution, if it exists or if you needed to make more assumptions in derivation.
5- What range of values of μ will result in a steady state solution for k = 1.
You need to submit a hardcopy report for the above five tasks. Don't write an essay, make it brief and clear. I expect the report to be a maximum of 3 pages (but it is ok if you go a bit above this). Also attach the printout of your code and evidence that you have run the code and obtained the results in part 4.
|
How much air pressure would be required to bubble air
: Assume a pipe has an inside diameter of 1 square inch. How much air pressure would be required to bubble air though 25 feet of water?
|
|
Prejudices manifest themselves in the workplace
: How do stereotypes and prejudices manifest themselves in the workplace? Do they become barriers to effective communication in the workplace? Do they make it difficult to accept people as individuals rather than as a group?
|
|
What would annual rates of return
: If a Japanese investor had purchased a mutual fund that imitated the Nikkei-225, what would her annual rates of return.
|
|
Used to predict future costs and profitability
: How can CVP Analysis be used to predict future costs and profitability? Describe how CVP Analysis is used, or could be used, at your current place of employment. If you have not worked for a company that might use CVP Analysis, you may choose a well-..
|
|
Write down the expressions for the total average delay
: Telecommunications System Modelling ECTE 962 - Write down the expressions for the total average delay (W) in the system, as well as other relevant indicators such as the size of queues at intersections. Clearly state any assumptions that you have ..
|
|
Job-order costing and process-costing systems
: What are the major differences between job-order costing and process-costing systems? Give an example of a well-known company that might use job-order costing, and an example of a well-known company that might use process costing. Explain why you hav..
|
|
What specific characteristics of indonesian culture
: What specific characteristics of Indonesian culture do you need to know in order to respond appropriately, with this particular cultural context in mind? If you were to respond, offer one specific sentence or strategy that you might take, given what ..
|
|
At what angle must the receiver be mounted
: An object is to be detected by reflecting light off a shiny surface. If the transmitter is mounted at a 60 degree angle, at what angle must the receiver be mounted?
|
|
What is the price of your product
: Pay particular attention to the sections on market segmentation, pricing, the low-tech segment, the high-tech segment, and the contribution margin. What is the price of your product
|