Reference no: EM13855775
Procedure and Questions:
- Start the Models of the Hydrogen Atom simulation.
- Turn on the White light gun. The white light shining into a transparent box containing hydrogen gas. This is the "?-box." The gas molecules have been ionized so hydrogen atoms are present, but the scientists cannot see these individual atoms (hence the "?). It is possible however to send the light into the box and record the light that is emitted from the box.
- To record the photons of light emitted from the transparent box check the "Show Spectrometer" box. Notice that the color of the photons being emitted from the box corresponds to a wavelength of UV, visible, or IR radiation.
- On the Slow...Fast slider, slide to the fast end of the scale.
- Run this simulation for at least 5 minutes on fast.
- Move the Slow...Fast slider all the way to Slow.
- Watch the photons carefully. Most of the light gun photons pass through the box of hydrogen unaffected. Occasionally something happens in the "?-box" and a photon is emitted. Note: The emission is recorded on the spectrophotometer.
- Take a snapshot of your experimental data--the emission spectrum. Use the camera at the bottom of the spectrophotometer.
Question 1:
Briefly identify
- the colors; and
- the approximate wavelengths of the H atomic spectrum in your "?-box." Also consider the relative amount of the light (stacked boxes).
Analyze the Experiment:
Examine the different models of hydrogen atom, consider the emission spectrum generated and compare it to the YOUR experimental emission spectra above. You will use the snapshot you took of the experimental spectrum wavelength.
Useful Formulas:
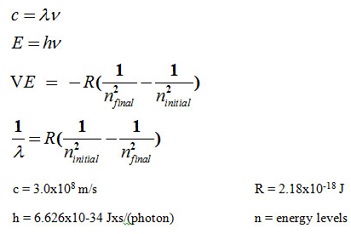
Questions 2 - 4:
- If a photon of monochromatic light has a wavelength of 94 nm, what is its frequency per second or Hz, s-1?
- What is the energy (J) of one photon?
- What is the energy of one mol of photons at 94 nm?
Dalton:
A brilliant model which is still useful but which was also wrong about an atom being non-divisible (smallest particle). However, it is still true that the atom is unique. I think the idea that the atom is the smallest particle that 'retains all the characteristics of that element' is still true. We now know that an atom consists of many smaller particles. In this class, we study the electrons, principally. "Valence Electrons" are the particles involved in chemical reactions.
Nuclear chemists and physicists study the structure of the nucleus. We will not spend time in this class - beyond the note that a nucleus contains protons and neutrons we studied in Unit 1. But, this is a very exciting time in physics. On March 14, 2013 the scientific community seemed to confirm the Higgs Boson particle - a/k/a/ as the "God particle". See https://news.discovery.com/space/higgs-boson-confirmed-130314.htm.
Take a couple of minutes to look at the "Billiard Ball" model.
Question 5:
Why doesn't anything appear on an emission spectrum in Dalton's "Billiard Ball" model?
Rutherford's Classical Solar System:
Be sure to slow this all the way down.
Question 6:
Which of these is correct? (Just highlight these in some way for me.)
- There is a nucleus containing a proton.
- There is an electron circling the nucleus, like a planet around a sun.
- The atom is not stable. The electron loses energy, spirals into the nucleus, and the atom is destroyed.
Comment: What does this mean to our model? It means that the electron must have its own 'ground-state' energy that resists/prevents the destruction of the atom.
Bohr Mode:
Run this simulation on fast for at least 5 minutes to compare to your snapshot of the experimental electromagnetic spectrum. Be sure to take a snapshot for later comparison to experimental results.
Questions 7:
Use transition from n = 2 to n = 3 (at 655 nm) to calculate the following:
- The frequency of the wavelength
- The Energy of the wavelength using Plank's Constant
- The Change in Energy, ΔE, of the transition (from n = 2 to n = 3)
- The predicted wavelength of energy absorbed (from n = 2 to n = 3) using Rydberg's equation
Using the Slow...Fast Slider, slow the speed down and answer the following questions. To aid in your analysis, click on "Show Electron Energy Diagram."
Questions 8 - 10:
- What happens to the electron when a photon hits the electron?
- Does anything happen in the Emission Spectrum when the photon hits (or is absorbed)?
- What happens IN THE EMISSION Spectrum when the photon returns to a lower energy level or the ground-state?
Question 11:
Compare the Experimental Emission Snapshot and Bohr Model Snapshot.
Is the Bohr Model spectrum 'right'? Briefly describe why or why not.
Schrodinger's Model:
You may need to run this simulation on fast for more than 5 minutes.
This is a more sophisticated model than Bohr's. When an electron interacts with the atom, the simulation shows the 'shape' of the orbital cloud. We have seen these as quantum numbers.
- When l = 0 (or s), the shape is a sphere;
- When l = 1 (or p), the shape is similar to a barbell.
- When l = 2 (or d) the shape is similar to a cloverleaf.
Notice that the shape is larger when the 'n' is larger.
Question 12:
(Highlight all correct answers.)
- There is a nucleus.
- The electron is a particle in a well-defined orbit.
- The position of the electron is represented in an ambiguous manner. Different areas are shaded.
Question 13:
The electron energy level diagram in the Schrodinger Model, is more complicated than the energy level diagram in the Bohr Model. What do the two areas at n=2 in the Schrodinger Model represent from our quantum numbers.
Question 14:
Compare the experimental spectrum snapshot to Spectrum generated by the Schrodinger Model. Is this model 'right'?