Reference no: EM13332178
1. Binding studies were carried out in which heparin was immobilized on the surface of cuvettes. The pH dependence of HPRG binding to heparin was investigated and the results are shown in Figure 2.1.
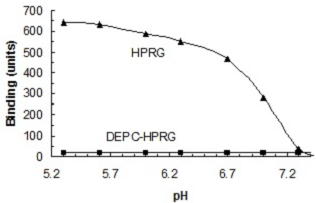
a. How is the binding of HPRG to heparin dependent on pH? Give structural reasons for the binding dependence. The structure of heparin is shown in Figure
2.2. NOTE: Figure 2.1 also serves as a titration curve for the His residues in R HPRG-what is the pK for these residues? Explain.
b. The same binding studies were carried out in which HPRG was reacted with diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC), a compound that specifically reacts with histidine residues. The reaction is shown in Figure 2.3. Explain the results.
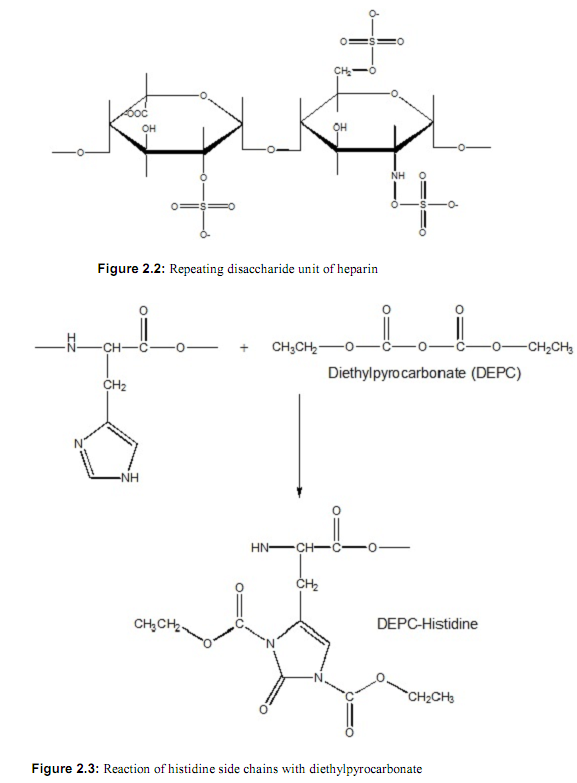
The pH-dependence of HPRG binding to unmodified heparin and heparin modified with DEPC.
2. The effect of transition metals on the binding of HPRG was investigated next. The ability of increasing concentrations of Cu2+ and Zn2+ to promote HPRG binding to heparin at pH = 7.3 was measured. The results are shown in Figure 2.4. In addition, the binding of HPRG to heparin in the presence of these ions was compared at various pH's. Figure 2.5 shows the comparison of binding of various concentrations of zinc ions at pH values ranging from 6.0 to 7.4. What is your interpretation of these results?
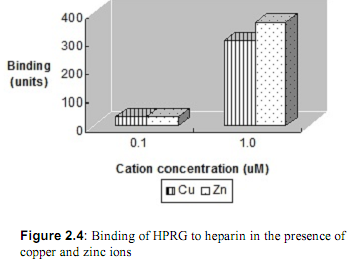
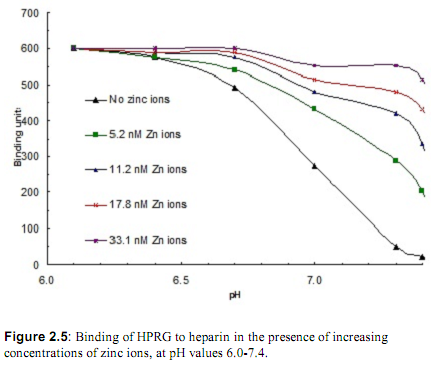
3. Local cellular pH can decrease from one-half to one pH unit depending on a variety of circumstances including ischemia, hypoxia, and inflammation due to lactic acidosis. In addition, metabolic acidosis is often one of the symptoms in complications following surgery. The investigators have proposed that HPRG acts to relieve the acidosis in these circumstances, possibly in synergy with Zn ions. Propose a simple model that explains the mechanism of pH regulation by HPRG.
4. Other plasma proteins have been studied for their ability to bind to glycosaminoglycans. One such protein is kininogen, which is a lysine-rich protein. Like HPRG, kininogen is able to bind to glycosaminoglycans, but this binding is far less sensitive to small fluctuations in physiological pH.
a. Why does kininogen bind to glycosaminoglycans easily?
b. Why is the binding of kininogen less sensitive to physiological pH changes?