Reference no: EM131134398
Part -1:
Question 1: As per Australian Standard AS 1170, what are the different types of loads that can be encountered by structures which need to be taken into account for their design?
Question 2: The process of designing structures involves combining the individual loads in different combinations and then taking the resultant of these load combinations and using it in the structural analysis.
a) Why do we undertake this analysis of load combinations on structures during the design process?
b) What are the provisions in AS 1170.2-2002 regarding load combinations for determining the strength in the design of the structure?
Question 3: Explain the principles of structural analysis.
Question 4: A hollow circular mild steel column of external diameter 300 mm and internal diameter of 250 mm carries an axial load of 1500 kN.
a) Determine the compressive stress in the column.
b) If the initial length of the column is 3.75 m, find the decrease in length of the column. Take E = 2 x 105 N/mm2.
Question 5: a) Define ‘Capacity Reduction factor' as applied to designing load bearing members in structures.
b) What is the necessity of using this factor while designing?
c) On what parameters does this factor depend on?
Question 6: The diameter of an aluminum rod serving as a compression member is 30 mm. The yield stress for aluminum is σy = 270 N/mm2 and the ultimate stress is σu = 310 N/mm2.
Find the allowable compressive force if the factors of safety with respect to the yield stress and the ultimate stress are 4 and 5 respectively.
Question 7: a) Define strain and provide its equation.
b) What are the different types of strains normally encountered in practice?
c) How are longitudinal strains different from bending strains?
d) Illustrate with a diagram the bending strains in a beam subjected to shear forces perpendicular to its principal axis.
Question 8: a) Briefly discuss strain development in rectangular sections.
b) In relation to reinforced concrete sections, write short notes with illustrations on:
i. Over-reinforced sections.
ii. Under-reinforced sections.
iii. Balanced sections.
iv. Which one of these section is preferred in practice from a safety point of view?
Question 9: Find the maximum bending stress produced in a round steel bar 50 mm in diameter and 9 m long due to its own weight when it is simply supported at the ends.
Steel weighs 77000 N/m3. (Use the Section Modulus, Z = πd3/32 and bending stress f = M/Z)
Question 10: a) Discuss various types of end conditions for beams with illustrations.
b) How do these end conditions affect the equilibrium conditions of displacement and moment in beams.
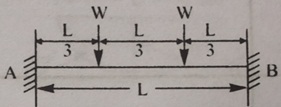
Question 11: Determine the end support reactions and maximum moment for the beam loaded as shown in the figure below.
Question 12: Using appropriate equations for deflection, slope, curvatureand moment, explain how the solution of beam deflection problemscan be carried out by direct integration of differential equations.
Question 13: Write a note with illustrations on the types of homogeneousboundary conditions in structural beams.
Question 14: a) Discuss the importance of the study of deflection in beams with respect to structures. (Discuss this with examples)
b) Which methods are available to engineers to study deflection in beams?
c) Which of the support conditionsprevent the displacement of beams at the respective ends. Illustrate with a figure. (This is discussed in the Module Reading Texts)
Question 15: a) Discuss the concept of the development of a bending moment in beams under the application of external loads.
b) What are the three equilibrium conditions for the static equilibrium of beams?
c) Using the method of sections, draw a neat illustration showing the development of axial force, shear, and bending moment at a beam section under external loads. (This is described in the Module Reading Texts)
Question 16: a) Define elastic strain energy as applied to structural members under external loading.
b) Identifythe expressions for elastic strain energy and strain energy density stored in members due to axial force and pure shear.
Question 17: Discuss the principle of Virtual Work and its applications for finding deflections in structural members through the Unit Load or Dummy Load Method.
Question 18: a) With the help of a diagram, discuss the development of flexural stresses in a beam section under external loading.
b) Specifythe flexure equation for calculating bending stresses and discuss its importance.
Question 19: A cast iron pipe of external diameter 60 mm and 10 mm thickness and 5m long is supported at its ends. The pipe carries a point load of 100 N at its centre.
Calculate the maximum flexural stress induced in the pipe due to the point load. (Take Section Modulus Z = I/c = π(D4 - d4)/32D)
Question 20: Identify the equations for the general expressions of normal and shearing stresses on any plane located by the angle θ and caused by a known system of stresses.
Specify the expression for locating the planes on which thelargest normal and shearing stresses occur.
Detail the expression for the largest shearing stress in terms of the principal normal stresses σ1 and σ2.
Question 21: a) Discuss the procedure for the design of a beamwhilst ensuring adequate structural safety of the structure.
b) How are the flexure and shear stress equations helpful while designing beams for structural adequacy? (This is described in the Module Reading Texts)
Question 22: a) What is a column?
b) Specifythe buckling or crippling load for acompression member.
c) Using Euler's theory of long columns, develop an expression for the crippling load of a column with both ends fixed.
Question 23: Specify the expressions for crippling loads in the following cases:
i. When both ends of the column are pinned (hinged).
ii. When one end of the column is fixed and the other end is free.
iii. When both ends of the column are fixed.
iv. When one end of the column is fixed, and the other end is pinned (hinged).
Question 24: With the aid of an illustration and Euler's equations,briefly discuss the load carrying capacity of columns as determined byexperimentation on real columns.
Question 25: a) Why is there a need to adopta Factor of Safety while designing columns?
b) Explain the criteriaan engineer uses to determine a particularFactor of Safety for a design.
Question 26: What is the equation for the fixed end moments (MABand MBA) in the following case?
(a) - WL/8
(b) - 3WL/16
(c) - 2WL/9
(d) - 19WL/12
(e) None of the above
Question 27: a) Discuss the assumptions which are made while deriving Euler's theory of long columns.
b) What are the limitations of this theory as applied to real columns?
c) What is the limiting value of the slenderness ratio of columns beyond which Euler's theory will not be valid?
Question 28: Choose the wrong statementfrom among the following choices.
The Principal Stresses are:
a) Planes on which maximum or minimum normal stresses occur, there are no shearing stresses.
b) Planes on which maximum or minimum shearing stresses occur, there are no normal stresses.
c) Shown to have an angle of 45owith the planes of maximum or minimum shearing stress.
d) Maximum shearing stress differs from the minimum shearing stress only in sign.
Part -2:
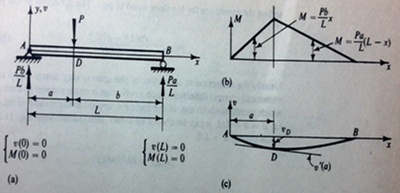
Question 1: A simply supported beam has a concentrated downward force P at adistance of afrom the left support, as shown in the figurebelow. The flexural rigidity EI is constant. Find the equation of the Elastic Curve by successive integration.
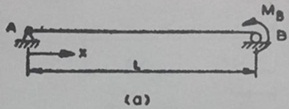
Question 2: Determine the rotations at A and B due to an applied moment MB on the beam, as shown in the figure below. Use the Method of Virtual Work.
Question 3: Find the strain energy stored per unit volume for the materials listed below when they are axially stressed to their respective proportional limits.
|
Material
|
Proportional Limit (N/mm2)
|
Modulus of Elasticity Proportional Limit (N/mm2)
|
|
Mild Steel
|
247
|
2.06 x 105
|
|
Aluminium
|
412
|
7.20 x 104
|
|
Rubber
|
2.06
|
2.06
|
Question 4: As shown in the figure below, find the downward deflection of the end C caused by the applied force of 2 kN in the structure. Neglect deflection caused by shear. Let E = 7 x 107 kN/m2.

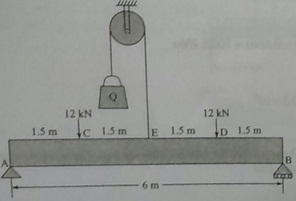
Question 5: For the loaded beam, as shown in the figure below, determine the magnitude of the counter weight Q for which the maximum absolute value of the bending moment is as small as possible. If this beam section is 150 mm x 200mm, determine the maximum bending stress. Neglect the weight of the beam.
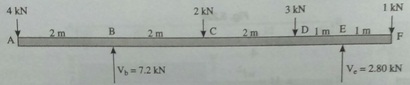
Question 6: A wooden beam with sectional dimensions of 150 mm x 300 mm, carries the loading as shown in the figure below. Determine the maximum shearing and bending stress for the beam.
Question 7: For the box beam shown in the figure below, determine the maximum intensity w of the distributed loading that can be safely supported if the permissible stresses in bending and shear are 10 N/mm2 and 0.75 N/mm2 respectively.

Question 8: A beam of rectangular section 450 mm wide and 750 mm deep has a span of6 metres. The beam is subjected to a uniformly distributed load of 20 kN per metre run (including the self-weight of the beam) over the whole span. The beam is also subjected to a longitudinal axial compressive load of 1500 kN.Find the extreme fibre stresses at the middle sectionspan.
Question 9: A hollow alloy tube 5 metres long with external and internal diameters equal to 40 mm and 25 mm respectively, was found to extend by 6.4 mm under a tensile load of 60 kN. Find the buckling load for the tube when it is used as a column with both ends pinned. Also find the safe compressive load for the tube with a Factor of Safety of 4.
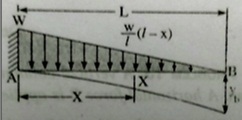
Question 10: A cantilever beamof length l carrying a distributed load varies uniformly from zero at the free end to w per unit run at the fixed end. Find the slope and downward deflection of the free end B.