Reference no: EM132603907
CSC2408 Software Development Tools - University of Southern Queensland
Linux Basics: Commands and Regular Expressions
Objective
The objective of this first assessment is to assess the understanding of Linux concepts, and knowledge of various command line interface (CLI) utilities, knowledge of regular expressions, and use of the manual pages to find appropriate options for the commands.
Question 1
Topic: Directories and files
Submission: Use the asciinema software to record the command line to a filename
userid_a1_q1.cast where userid is your student number.
Tasks: Perform the following tasks, starting in your home directory.
Set the PS1 shell variable to your student number so that your shell prompt looks like this:
u12345678=>
(if your student ID was u12345678)
Create the following directory structure, starting in your home directory
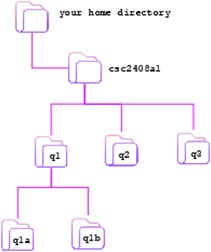
Figure 1: Directory structure for Question 1.2
Verify that the structure is correct using ls or other command-line utilities.
In your home directory, create a file called welcome.txt using vim con- taining the following text:
This is CSC2408 Software Development Tools
Without changing your current working directory, move the file wel- come.txt to the csc2408a1 directory.
Make a copy of the file welcome.txt called q1b.txt in the directory q1b.
Set permissions on the file welcome.txt so that the owner has only read permissions and the group and everyone else have no permissions.
Set the permissions on the directory q1b so that the owner can read the files in the directory, can read file contents in the directory, but cannot create or delete files in the directory. Set permissions for the qroup and everyone else have no permission.
Question 2
Topic: The Linux find command is quite useful and powerful. Examine the manual page for find.
Submission: Use the asciinema software to record the command line to a filename
userid_a1_q2.cast where userid is your student number.
Tasks: Perform the following tasks, starting in your home directory.
Set the PS1 shell variable to your student number so that your shell prompt looks like this:
u12345678=>
(if u12345678 was your student number)
Use a single find command to list all of the subdirectories in the direc- tory structure you created in Question 1, starting with csc2408a1, redirecting any standard errors to /dev/null
Use a single find command to search for all of the programs in the /usr/bin directory that have have SUID or SGID set. From the list produced, use ls to do long listings of the filenames to show the SUID or SGID is set.
Use a single find command to search for all files larger than 1 Mib in /usr/bin, printing the listing in a long format. Pipe this output to a sort command which will sort the list from largest to smallest.
Question 3
Topic: tar, gzip and more file operations.
Submission: Use the asciinema software to record the command line to a filename userid_a1_q3.cast where userid is your student number.
Tasks: Perform the following tasks, starting in your home directory.
Set the PS1 shell variable to your student number so that your shell prompt looks like this:
u12345678=>
(if u12345678 was your student number)
Change into the directory containing the welcome.txt file created in
Question 1.
Using tar, create a .tar archive containing the just welcome.txt file. Compress the resulting archive with gzip.
Move the resulting compressed archive to the q3 directory in the direc- tory structure created in Question 1 (see Figure1).
Without using gunzip (only using tar), view the table of contents of the compressed archive without extracting the files.
Extract the file from the compressed archive in the q3 directory.
Remove all of the files in the q3 directory.
You will be awarded 2 marks for correctly creating the compressed
.tar archive for submitting this assignment. The tar file should contain 1 file per question you have answered in this assignment (5 files if you have completed all questions). The commands used for this part (3.7) do NOT need to be included in your answer file/recording.
Question 4
Topic: Regular expressions
Submission: Place your answers in a text file called userid_a1_q4.txt where
userid is your student number.
Tasks: Below are 5 pairs of regular expressions. For each pair, describe in plain words what each regular expression will match, and high- light their difference by providing examples where one expression will match the example string, but the other will not.
For example, given the pair of regular expressions: ^abc. and ^abc$
your answer in the text file should be something like:
"Q4.1 a) The first regular expression will match a line that begins with the string of characters 'abc' followed by any single character (and may be followed then by zero of more characters). The second regular expression will match a line consisting of the string 'abc'
b) The first regular expression will match 'abcd', but the second ex- pression will not. The second expression will match the line 'abc' but not 'abcd'."
Note that sometimes you may only need to provide one example in the case that one expression will always match the examples but the other will not.
4.1 ab.*cd and abb*cd
4.2 [A-Z][_a-zA-Z0-9]* and [A-Z_][a-zA-Z0-9]*
4.3 [0-9]{4}-[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{3}} and [0-9]{4}-[0-9]{3,4}-[0-9]{3,4}
ab?cd and ab+cd
[abc]d and [^abc]d
Question 5
Topic: sed and regular expressions
Submission: Place your answers in a text file called userid_a1_q5.txt where
userid is your student number.
Tasks: As we saw in the course, sed is used to manipulate text using the matching of regular expressions. Below are 5 sed expressions. As- sume you have a file called myfile.txt. Describe in words what the sed expression will do. Use the manual pages for sed, and, if necessary, craft a text file with lines which will match the regular expressions, and test the command.
For example, if the sed expression is: sed 's/fox/ox/g' my- file.txt you see that the sed command is looking for the regular expression fox, you could create a myfile.txt with occurrences of fox and test the command.
Your answer in the text file would be something like:
"Q5.1 Expression: sed 's/fox/ox/g' myfile.txt
Answer: The command substitutes line by line all occurrences of 'fox' with 'ox' in myfile.txt"
sed '/^$/d' myfile.txt
sed -n '/There/ p' myfile.txt
sed -n 's/[A-Z]/&e/gp' myfile.txt
sed '32,45 s/[()]//g' myfile.txt
5.5 sed -E 's/([0-9]+)-([0-9]+)/\2:\1/g' myfile.txt
Attachment:- Software Development Tools.rar