Reference no: EM132334525
Modeling & Simulation Portfolio Assignment -
Task 1 - Creating scalar and array variables, Solving equations, Matrix Operations
Q1) Let
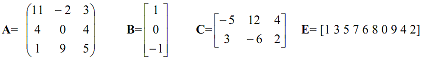
a) Write a command to arrange the element of the vector E in the ascending order.
b) Write a command to return the smallest element of vector E.
c) Write a command to delete 2nd column from matrix C.
d) Use left division to solve X = A-1B.
Q2) Use either solve or fzero, as appropriate, to solve the following equations:
(a) 8x + 3 = 0 (exact solution)
(b) 8x + 3 = 0 (numerical solution to 15 places)
(c) x3 + px + q = 0 (Solve for x in terms of p and q)
(d) ex = 8x - 4 (all real solutions). It helps to draw a picture first.
Task 2 - 2-D Plots, Getting Help
Q1) Use plot and/or ezplot, as appropriate, to graph following functions:
(a) y = x3 - x for -4 ≤ x ≤ 4.
(b) y = sin(1/x2) for -2 ≤ x ≤ 2. Try this one with both plot and ezplot. Are both results "correct"? (If you use plot, be sure to plot enough points.)
(c) y = tan(x/2) for -π ≤ x ≤ π,-10 ≤ y ≤ 10 (Hint: First draw the plot; then use axis.)
Q2) Help and documentation
Get help on the MATLAB function fprintf by using Type help fprintf command in the command window, or The Help Browser.
Explain the difference of the following fprintf commands and show their outputs, respectively:
Value = 123.4567e2;
fprintf('Value = %e\n', Value);
fprintf('Value = %f\n', Value);
fprintf('Value = %g\n', Value);
fprintf('Value = %12.4f\n', Value);
Task 3 - Script files, Program design with conditional statements and loops
Q1) Script files and input/output commands
Create a script file named task3_1.m and write the following sequence of commands (also called program) in this script:
radius = input('Enter the circle radius:\n');
Area = pi*radius^2;
Perimeter = 2*pi*radius;
fprintf('The area is %f \n', Area);
disp(['The perimeter is ' num2str(Perimeter)]);
Run the script and explain what do the sets of statement do? Take a screenshot of your command window to show one example how the program works.
Q2) Use if-elseif-else-end to calculate students' grade
Write a program in a script file named task3_2.m to read a numerical mark and then assign a letter grade to it according to the following table:
|
Mark
|
Letter grade
|
|
80 ≤ mark ≤ 100
|
High Distinction
|
|
70 ≤ marsk < 80
|
Distinction
|
|
60 ≤ mark < 70
|
Credit
|
|
50 ≤ marks < 60
|
Pass
|
|
0 ≤ mark < 50
|
Fail
|
|
mark < 0 or mark > 100
|
Invalid
|
The program asks the student to enter the numerical mark in command window; and then display the letter grade in command window.
For example: After running the program, a student could enter his mark in the command window. Then, the student's letter grade will be returned immediately.
Q3) Use for-end loop to calculate numerical equation
Write a program in a script file named task3_3.m to calculate the sum of the first n terms of the series:
k=1∑n(-1)kk2/1.2(2k+1)
The program asks the user to enter the number of n in command window; and then display the result in command window.
Run the script file for n = 4 and n = 20, respectively, and show the result in the command window like the following format:
>> task3_2
The result for n = 8 is 1.322298.
Q4) Use while-end, if-end, break commands to solve the numerical problem
Write a script file named task3_4.m that sums a sequence of random numbers (use randn) until the sum is greater than 10. If the random number generated is greater than 3, exit the loop immediately without doing the sum.
Display the sum of the random numbers and the last random number generated in command window when the program terminates. The display format may like this: >> task3_4.m
The sum of the random numbers is: 10.571232
The last random number generated is: 1.618112
Task 4 - Solving Engineering application with MATLAB
Q1) As shown in figure, a series RL circuit as shown acts as a low-pass filter.
i) Write down the transfer function for the low pass filter.
ii) Draw the simulink model for the low pass filter in part i (assume cut off frequency, fc = 100Hz and amplitude for the input signal is 10V)
iii) Draw the output waveforms when input signal (Vi) frequency is equal to 20Hz and 120Hz.
Q2) WikiPedia defines "Terminal Velocity" as follows: In fluid dynamics, an object is moving at its terminal velocity if its speed is constant due to the opposing force exerted by the fluid through which it is moving. A free-falling object achieves its terminal velocity when the downward force of gravity (FG) equals the buoyancy/resistance force of drag (Fd). This causes the net force on the object to be zero, resulting in an acceleration of zero. Mathematically, the terminal velocity of an object falling through air is given by
Vt = √(2mg/ρACd)
Where Vt = terminal velocity in m/s,
m = mass of the falling object in kg,
g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.8067 m/s,
Cd = drag coefficient, usually = ∼ 0.5
ρ = density of the fluid through which the object is falling, for air this is = 1.29 kg/m3
A = frontal area of the object
Write a MATLAB script file (call it terminal_velocity.m) that does the following: The first line in the script file (with your information filled in) should be:
- Use a basic for loop to repeat the following code twice
- Ask the user to enter the object's mass in kg.
- Ask the user to enter the object's frontal area in m2.
- Calculate the object's terminal velocity.
- Use appropriate comment statements in your script file.
- Print out the result using the fprintf command.
Clearly write down your MATLAB code and show the output you get.