Reference no: EM131477162
Q1. 1-1) Find the correct dollar values for (1) and (2) in the overdraft profile graph.
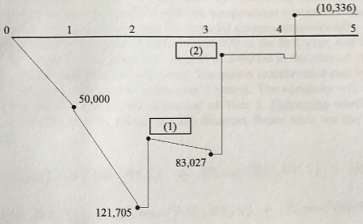
1-2) Plot a cash flow diagram for the costs and the payments received each month and calculate the sum of the present values of the cash flow. The discount rate is 2% per month. The equation to convert future values to present values is:
P = Fn/(1+i)n
Where, F is a future value after n periods at a discount rate of i.
Q2. The table below represents a contractor's overdraft requirements for a three-month project. Retainage is 10%, markup is 10%, and interest is 1% per month. The client is billed at the end of the month. Payment is received at the end of the next month. Retainage will be dropped out at last month of the construction period, and the accumulated retainage for the first two months will be paid to the contractor with the last payment. (Note: all calculated numbers should be rounded to integer numbers.)
|
|
Month
|
|
|
1
|
2
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
|
Overdraft
|
50,000
|
120,500
|
82,205
|
13,727
|
(10,336)
|
|
Interest
|
500
|
1,205
|
822
|
137
|
-
|
|
Total financed
|
50,500
|
212,705
|
83,027
|
13,864
|
(10,336)
|
Complete the overdraft table provided below.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
Expenditure
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Markup (10%)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total billed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Retainage (10%)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payment received
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total cost to date
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total amount billed to date
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total paid to date
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Overdraft
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest (1%)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Totam amount financed
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Q3. A corporation plans to invest in a small project which costs a one-time expenditure of $600,000 at Year 1. It intends to finance this project by borrowing from a local bank which requires the origination fee of $50,000. Compounded interest payments are made annually at a nominal interest rate of 7%/year with the repayment of the principal at the end of Year 5. The bank compounds the financial charges monthly. The MARR of the corporation is 15%.
3-1) Calculate the total present value of the cash inflows and outflows.
3-2) Based on the result from 3-1), find the minimum annual return over the five years that the corporation should generate to make the project viable economically (i.e., total PV = 0 after considering the annual return). (Note: use the discount factor table at the last page.)
|
Plot and compare bit error rate vs signal to noise ratio
: Plot and Compare Bit Error Rate Vs Signal to Noise Ratio for uncoded QPSK and trellis coded 8PSK with the same total power a reference, comparison on same plot
|
|
American participation in the vietnam war
: Summarize Johnsonâs justifications for American participation in the Vietnam War. In addition, explain how Johnson hopes to persuade.
|
|
Check the given statements are correct or incorrect
: Explain why each of the following statements is correct or incorrect: Diversification reduces risk because prices of stocks do not usually move exactly.
|
|
Crucial issues of the period as the tariff
: What role did the West play in such crucial issues of the period as the tariff, internal improvements, and the expansion of slavery?
|
|
Calculate the total present value of the cash inflows
: A corporation plans to invest in a small project which costs a one-time expenditure of $600,000 at Year 1. Calculate the total present value of the cash inflows
|
|
Increasing sense of self awareness
: The period 1825-1850 was marked by an increasing sense of self awareness among many Americans. Changes in society gave rise to questions about the nature.
|
|
What must the one-year interest rate be
: Suppose that the annual returns on two stocks (A and B) are perfectly negatively correlated, and that rA = 0.05, rB = 0.15, sA = 0.1, sB = 0.4.
|
|
Differentiate between primary and secondary data
: Assess the current position of an organization in relation to the public's perception, competitors and potential shifts in federal, state and local policies.
|
|
Calculate each security expected return
: Assume that an individual can either invest all of her resources in one of two securities A or B; or alternatively, she can diversify her investment.
|