Reference no: EM131018123
Midterm 3
Question 1: It is possible for a firm to experience diminishing marginal returns in the long-run.
A. True
B. False
Question 2: A monopolist profit maximizes by producing that level of output where marginal revenue equals marginal cost and charging a price greater than the average total cost of production.
A. True
B. False
Question 3: The market described by the following graph is consistent with the market being an oligopoly.
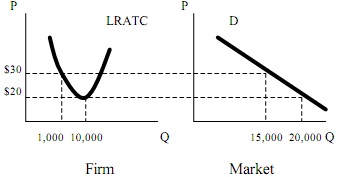
A. True
B. False
Question 4: In the long-run a firm will always earn zero economic profit, but it could have a positive accounting profit.
A. True
B. False
Question 5: If the total cost function is given by TC = 10,000 + 10Q + 85√Q , the associated total fixed cost and total variable functions are given by: TFC = 10,000 and TVC = 10Q + 85√Q respectively.
A. True
B. False
PART II: MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Question 6: K-Mart and Wal-Mart are considering establishing either 1 or 2 stores in a town. The payoff matrix, which gives the profits of each company, is as follows (profits are in million dollars):
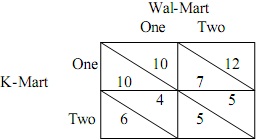
The upper triangle of each box corresponds to Wal-Mart's profits whereas the lower triangle shows K-Mart's profits. What is the equilibrium outcome in this game? K-Mart builds _____ store(s) and Wal-Mart builds ____ store(s).
A. (1, 1).
B. (2, 1).
C. (1, 2).
D. (2, 2).
E. There is no equilibrium in this game.
Question 7: Suppose the demand and supply in a perfectly competitive market are as follows:
Demand: P = 20 - 0.005Q
Supply: P = 0.005Q
A representative firm in the perfectly competitive market has a marginal cost, MC = 10Q. In the short run, the profit-maximizing output is _____ units for an individual firm and the equilibrium price is _____ .
A. (10,10)
B. (10,100)
C. (1,10)
D. (1,100)
E. (0.1,10)
Question 8:
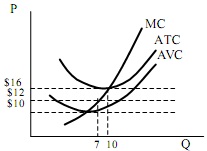
The figure above shows the cost structure of a representative firm in a perfectly competitive market. Suppose the current market equilibrium price is $12. Which of the following statements is FALSE?
A. The marginal revenue curve for the firm is P = $12.
B. There is a negative economic profit in the short run.
C. The long-run equilibrium price is $16.
D. In the short run, this firm will shut down the business and leave the market.
E. In the long run, if there are 100 firms staying in this market, the equilibrium quantity will be 1,000 units.
Question 9: Which of the following is TRUE?
A. A monopolistically competitive firm does not produce at its minimum ATC in the long-run.
B. A monopolistically competitive firm cannot successfully maintain positive economic profits in the long-run.
C. Barriers to entry make it possible for monopolies to earn positive economic profits in the long-run.
D. (A) and (C).
E. (A), (B) and (C).
Question 10: A monopolist has cost function TC = 10 + 2Q. Demand in this market is given by the equation Q = 14 - P. If this monopolist can charge only a single price, its profit in the short run will be:
A. -8
B. 10 C. 26
D. 34
E. 46
Question 11: Which of the following statements is NOT a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market?
A. The equilibrium output is both allocatively and productively efficient.
B. While firms in a perfectly competitive market can make positive, zero, or negative economic profits in the short-run, they have to make zero economic profits in the long-run.
C. Marginal revenue for a perfectly competitive firm is equal to the market price because firms in a perfectly competitive market are price takers.
D. In the short-run, a perfectly competitive firm will continue production as long as it can cover its total variable costs.
E. There are many firms in a perfectly competitive market that produce differentiated products.
Question 12: A regulated natural monopolist practicing average cost pricing
A. makes zero economic profit.
B. produces an allocatively inefficient level of output.
C. produces the largest quantity possible while still enabling the firm to cover its total costs. D. all of the above.
E. none of the above.
Question 13: Which of the following is an example of perfect price discrimination?
A. lower air fares for customers willing to stay over a Saturday night.
B. discount movie tickets for children and senior citizens.
C. discounts for seats with an obstructed view in a theater.
D. higher phone rates on weekdays than on weekends. E. none of the above.
Question 14: Which of the following statements about cost functions is TRUE?
A. If there is an increase in total fixed costs (TFC), average variable costs (AVC) will increase.
B. A firm that has increasing average costs as output expands experiences increasing returns to scale.
C. Marginal cost is not affected by changes in fixed costs.
D. As the level of output increases, the difference between average total cost (ATC) and average variable cost (AVC) widens.
E. If marginal cost is less than average variable cost, then the average variable cost is increasing.
Question 15: A monopolist sells a single product and its consumers fall into two groups, group A and group B. The marginal cost of producing the good is constant at $2 and is equal for both groups. The two graphs below depict the demand curves and the marginal revenue curves for each of the two groups:
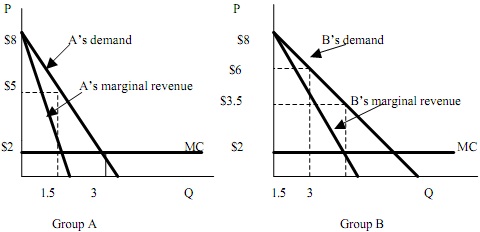
Suppose that the monopolist can distinguish between the two groups and engages in price discrimination. Which of the following is true if the monopolist maximizes its profits?
A. The price charged to group A is greater than the price charged to group B. The quantity sold to group A is greater than the quantity sold to group B.
B. The price charged to group A equals the price charged to group B. The quantity sold to group A equals the quantity sold to group B.
C. The price charged to group A is greater than the price charged to group B. The quantity sold to group A is less than the quantity sold to group B.
D. The price charged to group A is less than the price charged to group B. The quantity sold to group A is greater than the quantity sold to group B.
E. The price charged to group A is less than the price charged to group B. The quantity sold to group A is less than the quantity sold to group B.
Question 16: Which of the following statements about market structures is TRUE?
A. All unregulated firms, regardless of the type of the market they are in, are productively efficient.
B. A perfect price discriminating monopoly is allocatively efficient.
C. Monopolistically competitive firms do not operate at the minimum cost per unit in the long- run.
D. Oligopolistic markets are characterized by strategic interactions. E. All of the above
Question 17: The following table provides information about long-run average cost curve of a firm:
|
Q
|
LRAC
|
|
100
|
50
|
|
200
|
43
|
|
300
|
39
|
|
400
|
39
|
|
500
|
44
|
|
600
|
52
|
Which of the following statements is TRUE about this firm?
A. For the first 300 units of output, this firm has decreasing returns to scale.
B. For output levels between 300 and 400, the firm has constant returns to scale.
C. For output levels greater than 400, the firm has increasing returns to scale.
D. This cost structure is an example of natural monopoly.
E. All of the above
PART III: PROBLEM
Please write legibly. Make sure to show ALL your work. You may not receive any credit if you fail to show your work. Put your answers for each part in the respective blanks provided.
Suppose a monopoly faces the following demand curve for its product:
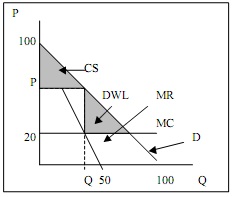
The equations for the demand curve and the marginal revenue curve are given as follows:
D: P = 100 - Q
MR: MR = 100 - 2Q
From the demand curve the monopolist obtains its marginal revenue curve, which has been also drawn in the graph above. Note that both curves are linear.
A. Suppose the monopolist has constant marginal costs of production given by MC = 20 and total costs given by TC = 20Q + 1000 . Using this information and the information above on the graph mark:
- The monopolist's quantity Q
- The monopolist's price P
- Draw the MC curve Then, numerically calculate:
- The monopolist's optimal quantity (Q) = ______
- The price the monopolist will charge (P) = _____
B. Find the consumer surplus that is associated with the monopolist's optimal price/quantity combination. On the graph:
- label the consumer surplus for the monopolist
Calculate:
- the dollar value of the consumer surplus if the firm is a monopolist equals ____ .
- the dollar value of the consumer surplus if this was a perfectly competitive industry equals ___ .
C.
- Discuss the efficiency properties of the monopolist's optimal price/quantity combination.
- On the graph label the area that corresponds to dead-weight loss.
- The dollar value of the dead-weight loss equals ______ .
D.
- Suppose now that the government decides to auction off a license to be the monopoly provider of this good for one year. Using all the information given above, decide how much the monopolist that we have analyzed in parts (a), (b), and (c) would be willing to pay for this license.
- Suppose the government gives consumers the auction proceeds (thus augmenting their consumer surplus). Rank the following three choices according to consumers' preferences where 1 is the best choice from the consumers' point of view and 3 is the worst choice from their point of view:
____ Firm is a monopoly
_____ Market is perfectly competitive
_____ Monopolist's rights are auctioned off with consumers receiving this payment.
Make sure you support your argument with a numerical analysis using the information above and your answer for part (B)