Reference no: EM13681897
Assignment:
Question 1. Suppose your company's method of making decisions under risk is "making the best out of the worst possible outcome." What rule would you be forced to follow?
Choice making is a science and in view of immaculate standards of likelihood and/or subjective paradigm of the choice taker. The entire issue begins when we are indeterminate about conceivable future occasions and in this manner about the profits we can get as profits depend for the occasion that really happens later. Along these lines, the danger is in view of instability about the real result, best case scenario we have a menu of choices to browse in the present. In this menu we may have probabilities joined to every conceivable choice/ state. Whether we have these probabilities or not will be not basic; what is vital is the subjective methodology of the chief. A worrier will attempt to boost the most exceedingly awful conceivable result, utilizing a MAXIMIN methodology/tenet. The inverse is the MAXIMAX approach or the hopeful methodology when the choice picked is in view of most astounding out of greatest result from every alternative. This is additionally called 'best of the best' choice.
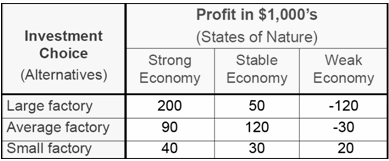
In the table over a doubter will first pick the least result under every alternative/elective. These are -120 (expansive manufacturing plant), -30 (normal production line) and 20(small industrial facility). Out of these the most extreme - 20 is picked so that a SMALL industrial facility is picked as the choice to embrace.
The hopeful person will pick a LARGE industrial facility. He will first pick the most elevated result under every choice/elective. These are 200 (vast production line), 120 (normal processing plant) and 40(small industrial facility). Out of these the most extreme - 200 is picked so that a LARGE production line is picked as the choice to attempt.
This sample obviously demonstrates that it is so essential to pick the subjective way to choice making as the picked alternative is basically reliant on the methodology .
Question 2. "A portfolio manager needs to pick winners-assets or securities with high expected returns and low risk." What is wrong with this statement?
A portfolio supervisor needs to pick "winning portfolios" as opposed to individual stocks that are "champs". The execution of a portfolio reflects associations among stocks and additionally the execution of individual stocks. For example, the instability of a portfolio is lower than the normal of the volatilities of the individual stocks. An effective portfolio director will pick a portfolio that either gives the most noteworthy conceivable come back to a speculator's fancied level of danger or gives the least conceivable danger to a financial specialist's wanted level of return.
Question 3. Do you favor anti-gouging laws as a means of protecting consumers from high prices following natural disasters, such as Hurricane Katrina in New Orleans? If so, why? If not, why not?
Value gouging alludes to a trek in the cost of key things after a regular fiasco has hit. This may happen when the vender climbs costs all alone realizing that the supplies are much lower because of the calamity while interest will be high as individuals have no choice with the exception of the neighborhood retailer. This may likewise happen on the grounds that the interest for fundamental things may climb in foresight of proceeded with interruption of ordinary life after the calamity has passed. There is a feeling of frenzy in the business sector that influences request and supply bends antagonistically. For instance, when costs are raised by suppliers it powers theory about further treks; this reasons interest to climb, which further fills the value trek. Additionally, It prompts fake deficiencies, as individuals begin storing key things. The deficiency exists in light of the fact that request is climbing yet supply is most certainly not. This is fake in light of the fact that buyers have an unnatural appeal and have supplied up past their genuine ordinary interest levels.( because of instability and feeling of frenzy) The dispersion of existing supply ( which was sufficient to coddle old interest levels)becomes unbalanced giving a feeling that there is a lack.
The laws against gouging are established in security of purchaser diversions. Unmistakably the interest is higher and a balanced/market system manages that cost will be higher. Plainly there is no productivity misfortune because of higher costs as these are business sector clearing levels. However since this higher interest is because of sudden reasons that involve a hardship on individuals the high costs can be viewed as' dishonest' from a social point of view. Consequently I backing these laws when the reason is a sudden regular fiasco. In the event that gouging is taking into account different reasons that don't include sudden hardships because of common catastrophes then I would not help any law against it as the higher value charged is sound ( from vender's perspective) and it additionally upholds productivity in the business system as it likens request with supply.
Question 4. How does a price ceiling undermine the rationing function of market-determined prices? How could rationing coupons insure that consumers with the highest values get the limited amount of a good supplied when government prices ceilings create shortages?
The roof or top presence on costs presumes that, for given economic situations, the costs would be higher. In a focused business, a dealer would diminish its costs to undercut different merchants and pull in more clients. The dealers who have lower efficiencies and higher costs would be stopped from the business, to the banquet of the clients.
Because of generation issues, if there is any lack of items when contrast with interest, then the cost of the item would climb. At that point the item would be determined to the most intrigued or willing clients and the venders would keep offering the item the length of clients were intrigued. On the off chance that the cost of the item rose to the level that request dropped, then the merchants comprehend that their endeavors will never again be considered, and would stop looking for the item. The dealers will confirm that harmony has been arrived at their expenses and costs.
With a roof on the costs, the vast majority of the merchants will have issue in supplying the item, as the costs the administration permitted to alter won't permit getting the fancied benefits. This will prompt the restriction of item accessibility. On the off chance that the item is coveted, clients look for the item. At the point when merchants because of the roof is confronted the possibility of not having the capacity to take care of the expenses and no less than two costumers who are envious, this dealer may put the item for offer. The merchant may charge an expense for spotting the item or different charges. The client then will get the item.
This can be similar to the discoverer's charges and different charges that permit having penthouse condo in New York for just few hundred dollars every month. The cost is rent controlled expense, however just rich individuals can get to the level of consenting to the arrangement. This is the manner by which the rich individuals in New York get the penthouse condo for simply $300 every month.
By putting value controls, the legislature tells the supplier that he ought not value the item over the certain level. With apportioning, the legislature is concealing the sum from the client. The clients get free coupon from Uncle Sam, they turns into the supplier, who then recovers the coupon for Uncle Sam whatever decides to pay. Clients then ask why the supplier has used up the item.
Proportioning simply shrouds the value controls. As talked about prior, valuing system is still undercut, however the client may be oblivious regarding what happening, and at times simply the urgent or those rich individuals enough to pay off law authorization can get the items or merchandise.
Question 5. Suppose the manager of a firm has a utility function for profit of:
The manager is considering a risky project with the following profit payoffs and probabilities.
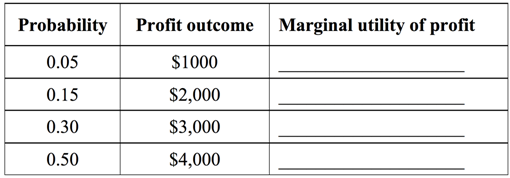
a. Calculate the expected profit.
b. Calculate the expected utility of profit.
c. Fill the blanks in the table showing the marginal utility of an additional $1,000 of profit.
d. The manager is risk ______ because the marginal utility of profit is _______.
The manager receives an offer from another party to buy the rights to the risky project described above. This party offers the manager $3,200, which the manager believes will be paid with certainty.
e. The utility of $3,200 is __________.
f. Comparing the utility of $3,200 with the expected utility of the risky project, what should the manager do if the manager wishes maximize expected utility of profit? Explain.
g. Is your decision in f. consistent with the manager's attitude toward risk as it is reflected by the utility function for profit? Explain.
h. Is the decision consistent with the mean-variance rules for decision making under risk? Explain.