Make-or-Buy Decisions
Usually, before a new item is indented in the purchase order, managers conduct a make-or-buy analysis. Through this analysis, managers determine whether it is more economical to produce the item in-house or purchase it from external vendors. In some cases, a firm's production department may be able to produce items in-house at lower cost, with higher quality, and deliver them faster than external vendors. Purchasing managers take inputs from production engineers during the make-or-buy analysis. A typical make-or-buy decision is based on a break-even analysis.
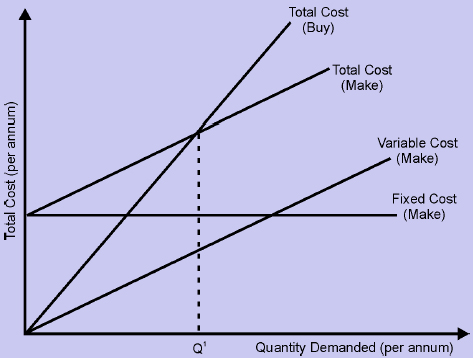
As shown in Figure 11.2, there is no fixed cost associated with purchasing material and the total cost of buying is the product of price per unit (P) and the number of units procured (Q), i.e.
Total Cost buy = P ´ Q
If the item is made in-house, the organization incurs a fixed cost, say F, for installing the necessary equipment and facilities. It also incurs variable production cost, which is equal to the unit variable cost (V) times the number of units demanded (Q).
Total Cost make = (VQ) + F
In Figure 11.2, we can see that at break-even point, the total cost of buying is equal to the total cost incurred by making the item in-house. Let us assume that Q1is the demand to reach break-even point.
P´Q1=(VQ1) + F
Q1 = F/(P-V)
So if the annual demand for the product is less than Q1, the total cost of purchasing the product from an external vendor will be less than the total cost of making the product in-house. If demand is greater than Q1, the total cost of making the product in-house will be less than the cost of purchasing it from an external vendor. Managers use this analysis to determine if the purchase cost of a product from an external vendor is less than the cost of producing it in-house.
Figure : Make-or-Buy Analysis
Cost is not the only factor influencing the purchasing decision. Before making make-or-buy decisions, organizations take into account factors such as the availability of raw materials in the long-run, the ability to monitor and control quality, etc. Many organizations opt for external suppliers because of their specialized skills in producing the required products. Suppliers maintain high standards in quality and ensure timely delivery because if they do not do so, they would lose the contract.
Organizations usually opt for in-house production for the following reasons:
-
To have control over all the value chain activities
-
To put excess plant capacity to productive use
-
To ensure that the design of a product is kept a secret
Organizations usually opt for outsourcing of a material for the following reasons:
-
To take advantage of knowledge and expertise of suppliers
-
To avoid incurring infrastructure costs when the quantity required is too low to justify in-house production
-
To maintain a multiple source policy
Many large organizations maintain both make and buy capabilities to ensure delivery of materials when suppliers are unable to meet their commitments (due to strikes, production problem, etc.).
Problem
Raj Metals can purchase brass plates for Rs.30 per unit or produce it in-house where the associated fixed and variable costs are Rs.50,000 and Rs.20 respectively. If the demand for this component is 5000 units per annum, ascertain whether it is economical to make the product in-house rather than sourcing it.
Solution
Given:
Demand = 5000 units
F = Rs. 50,000
V = Rs. 20
P = Rs.30
Q = 5000
If the item is made in-house, the organization incurs a fixed cost, say F, on installing the necessary equipment and facilities. It also incurs a variable production cost, which is equal to the unit variable cost (V) times the number of units demanded (Q).
Total Cost to manufacture = (VQ) + F
= (23 x 5000) + 50000
= 115,000 + 50000 = 165,000
The total cost of buying is the product of price per unit (P) and the number of units procured (Q), i.e. Total Cost if purchasing = P ´ Q
= 5000 x 30 = 150,000
As the cost to produce the item is more than the cost of purchasing it, it is not economical for the company to produce the component in-house.
Email based Operations Management assignment help - homework help at Expertsmind
Are you searching Operations Management expert for help with Make-or-Buy Decisions questions? Make-or-Buy Decisions topic is not easier to learn without external help? We at www.expertsmind.com offer finest service of Operations Management assignment help and Operations Management homework help. Live tutors are available for 24x7 hours helping students in their Make-or-Buy Decisions related problems. We provide step by step Make-or-Buy Decisions question's answers with 100% plagiarism free content. We prepare quality content and notes for Make-or-Buy Decisions topic under Operations Management theory and study material. These are avail for subscribed users and they can get advantages anytime.
Why Expertsmind for assignment help
- Higher degree holder and experienced experts network
- Punctuality and responsibility of work
- Quality solution with 100% plagiarism free answers
- Time on Delivery
- Privacy of information and details
- Excellence in solving Operations Management questions in excels and word format.
- Best tutoring assistance 24x7 hours