Simpson's Rule - Approximating Definite Integrals
This is the last method we're going to take a look at and in this case we will once again divide up the interval [a, b] into n subintervals. Though, unlike the preceding two methods we want to require that n be even. The cause for this will be obvious in a bit. The width of every subinterval is,
Δx = b - a / n
In the Trapezoid Rule (explain earlier) we approximated the curve along with a straight line. For this Rule (Simpson's Rule) we are going to approximate the function along with a quadratic and we're going to need that the quadratic agree with three of the points from our subintervals. Below is a drawing of this using n = 6. Every approximation is colored in a different way thus we can see how they actually work.
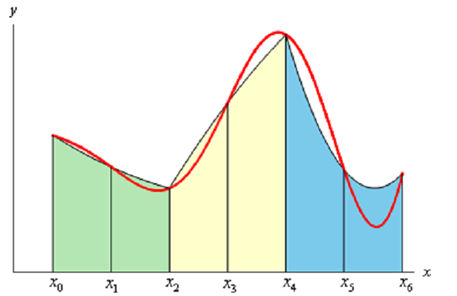
Note: In fact each approximation covers two of the subintervals. This is the cause for requiring n to be even. A few approximations look much more like a line after that a quadratic, but they really are quadratics. As well note that some of the approximations do a better job as compared to others. It can be illustrated that the area under the approximation on the intervals [xi -1, xi] and [xi , xi+1] Δ is like this:
Ai = Δx / 3 (f(xi-1)+4f(xi) + f (xi+1))
If we make use of n subintervals the integral is then approximately,
∫ba f (x) dx ≈ Δx / 3 (f(x0) + 4f (x1) + f (x2) + Δx / 3 (f (x2) + 4f (x3) + f (x4)) + ....+ Δx / 3 (f (xn-2) + 4f (xn-1) + f (xn))
On simplifying we reach at the general Simpson's Rule.
∫ab f (x) dx ≈ Δx / 3 [(f(x0) + 4f (x1) + 2f (x2) .... + 2f (xn-2) + 4f (xn-1) + f(xn)]
In the above case notice that all the function evaluations at points along with odd subscripts are multiplied by 4 and every function evaluations at points with even subscripts (apart from for the first and last) are multiplied by 2. If you can keep in mind this, this is a quite easy rule to remember.