Serialisability:Any schedule that makes the similar results as a serial schedule is known as a serialisable schedule. But how can a schedule are determined to be serialisable or not? In other words, other than giving values to several items in a schedule and checking if the results obtained are the similar as those from a serial schedule, is there an algorithmic way of determining whether a schedule is serialisable or not?
The basis of the algorithm for serialisability is engaged from the notion of a serial schedule. There are 2 possible serial schedules in case of two transactions (T1- T2 OR T2 - T1). Likewise, in case of 3 parallel transactions the number of possible serial schedules is 3!, i.e., 6. These serial schedules can be:
T1-T2-T3 T1-T3-T2 T2-T1-T3
T2-T3-T1 T3-T1-T2 T3-T2-T1
Using the notion of precedence graph, an algorithm can be creates to verify whether an interleaved schedule is serialisbale or not. In this graph, the transactions of the schedule are showed as the nodes. That this graph also has directed edges. An edge from the node showing transactions Ti to node Tj means that there exists a conflicting operation among Ti and Tj and Ti precedes Tj in some conflicting operations. It has been cleared that a serialisable schedule is the one that have no cycle in the graph.
Specified a graph with no cycles in it, there have to be a serial schedule corresponding to it. The steps of constructing a precedence graph are:
1. Make a node for each transaction in the schedule.
2. Search the precedence relationships in conflicting operations. Conflicting operations are (read-write) or (write-read) or (write-write) on the similar data item in two dissimilar transactions. But how to find them?
- For a transaction Ti which reads an item A, find a transaction Tj that writes A later in the schedule. If such a transaction is found, illustrate an edge from Ti to Tj.
- For a transaction Ti which has written an item A, find a transaction Tj later in the schedule that reads A. If such a transaction is found, illustrate an edge from Ti to Tj.
- For a transaction Ti which has written an item A, find a transaction Tj that writes A later than Ti. If such a transaction is found, illustrate an edge from Ti to Tj.
3. If there is any cycle in the graph, the schedule is not serialisable, or else, find the equivalent serial schedule of the transaction by traversing the transaction nodes beginning with the node that has no input edge
Let us use this algorithm to check whether the schedule as shown in Figure is Serialisable. Figure shows the needed graph. Please note as for every step 1, we draw the two nodes for T1 and T2. In the schedule shown in Figure, please note that the transaction T2 reads data item X, which is then written by T1, therefore there is an edge from T2 to T1 (clause 2.1). Also, T2 reads data item Y, which is then written by T1, therefore there is an edge from T2 to T1 (clause 2.1). Though, that edge already exists, so we do not require to redo it. Please note that there are no cycles in the graph, therefore, the schedule shown in Figure is serialisable. The equal serial schedule (as per step 3) would be T2 followed by T1.
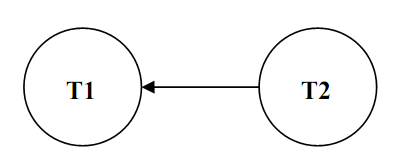
Figure: Test of Serialisability for the Schedule of above figure.
The two edges that exist among nodes T1 and T2 are:
- T1 writes X which is later read by T2 , so there exists an edge from T1 to T2.
- T2 reads X which is later written by T1, so there exists an edge from T2 to T1.
Therefore the graph for the schedule will be:
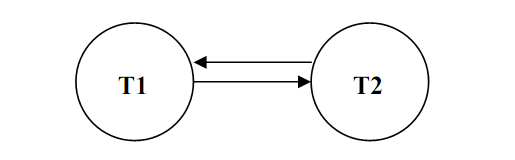
Figure: Test of Serialisability for the Schedule
Please note that the graph above has a cycle T1-T2-T1, thus it is not serialisable.