For a queue a physical analogy is a line at booking counter. At booking counter, customers go to the rear (end) of the line & customers are attended to several services from the front of the line. Unlike stack, customers are inserted at the rear end & deleted from the front end into a queue (FIFO).
In computer science, an instance of the queue is print jobs scheduled for printers. These jobs are maintained into a queue. The job fired for the printer first gets printed first. Similar is the scenario for job scheduling in the CPU of computer.
Like a stack, usually a queue also holds data elements of the similar type. Usually We graphically display a queue horizontally. Figure demonstrates a queue of 5 characters.
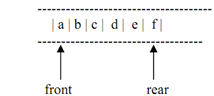
Figure: A queue of characters
In a queue the rule followed is that elements are inserted at the rear & come off of the front of the queue. After the insertion of an element to the above queue, the position of rear pointer alters as illustrated below. Now the rear is pointing to the new element 'g' added at the rear of the queue.
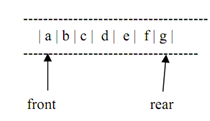
Figure: Queue of above figure after addition of new element
After the elimination of element 'a' from the front, the queue alters to the following along with the front pointer pointing to 'b'.
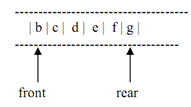
Figure: Queue of figure 5.2 after deletion of an element
Algorithm for insertion of an element to the queue
Step 1: Create a new element to be inserted
Step 2: If the queue is empty, then go to
Step 3, else perform step 4
Step 3: Make the front & rear point this element
Step 4: Insert the element at the end of the queue and shift the rear pointer to the lately added element.
Algorithm for deletion of any element from the queue
Step 1: verify for Queue empty condition. If queue is empty, then go to step 2, else go to step 3
Step 2: Message "Queue Empty"
Step 3: Delete the element through the front of the queue. If in the queue it is the last element, then carry out step a else step b
a) make front & rear point to null
b) Shift the front pointer further on to point to the next element in the queue