Hill Climbing - artificial intelligence:
As we've seen, in some particular problems, searching the search path from primly to goal state is the point of the exercise. In another problem, the path and the artefact at the end of the path are both important, and we often try to find optimal solutions. For a sure set of problems, the path is immaterial, and finding a suitable artefact is the sole purpose of the search. In these types of cases, it doesn't matter whether our agent searches a path for ten or thousand steps, so long as it finds a solution in the end.
Take an example of the 8-queens problem, where the job is to find an arrangement of 8 queens on a chess board likewise that no one can "take" another (one queen can take another if it's on the same horizontal, vertical or diagonal line). A solution to this problem is:
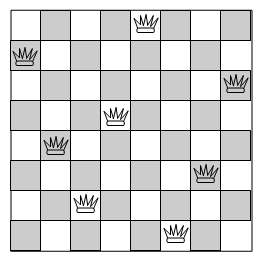
One way to describe this problem is with states where there are many queens (1 to 8) on the board, and an action is to add a queen in that kind of way that it can't take another. Depending on your method, you can find that this search requires much back-tracking, for example , towards the end, you find that you just simply can't put the last queens on anywhere, so you have to move one of the queens you put down earlier (you go back-up the search tree).
Another way of specifying the problem is that the states are boards with eight queens already on them, and a stroke is a movement of one of the queens. In this particular case, our agent might be use an evaluation function and do hill climbing. i.e., it measures the number of pairs of queens where one can take the other and only moves a queen if that movement reduces the number of pairs. When there is an option of movements both resulting in same amount of decrease, the agent may select one arbitrarily from the option. In the 8-queens problem, there are just 8 * 56 = 448 probable ways to move one queen, so our agent only has to calculate the evaluation function 448 times at each stage. If it just selected moves where the situation with respect to the evaluation function improves, it is doing hill climbing (or gradient descent if it's better to think of the agent going downhill rather than uphill).
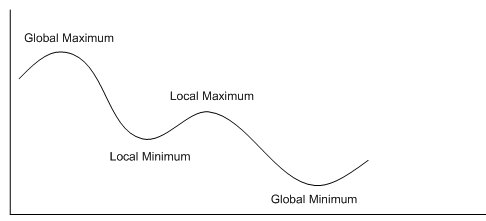
A general problem with this search method is local maxima: the search has not yet reached a solution, but it can just go downhill in terms of the evaluation function. I.e., we might get to the stage where only 2 queens may take each other, but moving any queen increases this number to at least three. In such a cases, the agent may do a random re-start whereby they randomly choose a state to start the complete process from again. This search scheme has the appeal of never requiring storing more than one state at any one time (the part of the hill the agent is on). Russell and Norvig make the analogy that this kind of search is like trying to climb Everest in the fog with amnesia, but they do concede that it is frequently the search strategy of option for some industrial problems.Local/Global Maxima/Minima are represented in the diagram below: