Q. Explain about Interrupt-Processing Sequence?
The occurrence of an interrupt fires a numbers of events both in processor hardware and software. Figure below displays a sequence.
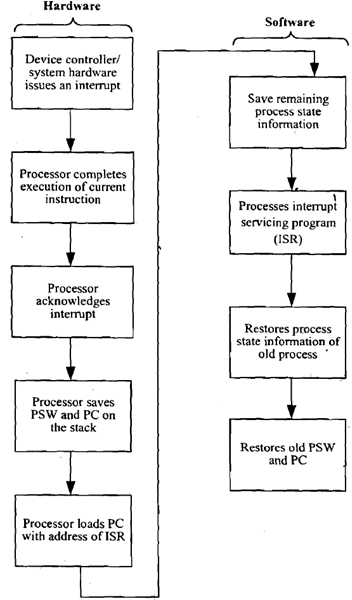
Figure: Interrupt-Processing Sequence
When an I/O device completes an I/O operation, the below sequence of hardware events takes place:
1. The device issues an interrupt signal to processor.
2. Processor completes execution of current instruction before responding to interrupt.
3. Processor tests for interrupts and sends an acknowledgement signal to device that issued the interrupt.
4. The minimum information needed to be stored for task being currently executed before CPU starts executing interrupt routine (using its registers) are:
(a) Status of processor that is contained in register known as program status word (PSW), and
(b) Location of next instruction to be executed, of currently executing program that is contained in program counter (PC).
5. Processor now loads PC with entry location of interrupt-handling program which will respond to this interrupting condition. Once PC has been loaded, processor proceeds to execute next instruction, which is the next instruction cycle that begins with an instruction fetch. Since the instruction fetch is determined by contents of the PC, result is that control is transferred to interrupt-handler program. The execution results in the subsequent operations:
6. PC & PSW relating to interrupted program have already been saved on system stack. Additionally the contents of processor registers are also needed to be saved on stack which are used by called Interrupt Servicing Routine since these registers may be modified by interrupt-handler. Figure (a) displays a simple illustration. Here a user program is interrupted after instruction at location N. Contents of all of registers and address of next instruction (N+1) are pushed on to stack.
7. Interrupt handler next processes interrupt. This involves determining of event which caused the interrupt and also status information relating to I/O operation.
8. When interrupt processing is finish, saved register values are retrieved from stack and restored to registers that are displayed in Figure (b).
9. Final step is to restore values of PSW and PC from stack. Consequently the instruction to be executed will be from previously interrupted program.