Conditional branch Instruction
When these type of instructions are executed, they transfer control of execution to the address mention relatively in the instruction, provided the condition implicit in the op code is satisfied, or else, the execution continues in sequence. Here, the conditions mean the status of condition code flags. These types of instructions remain unaffected from any flag. The address has to be mention in the instruction relatively in the terms of displacement which ought to be lie within range -80H to 7FH (or -128 to 127) bytes from the address of the branch instruction. In other terms, only short jumps may be implemented by using the conditional branch instructions. A label can represent the displacement, if it lies within the above mention range. The different 8086/8088 conditional branch instructions and their operations are listed in the following Table.
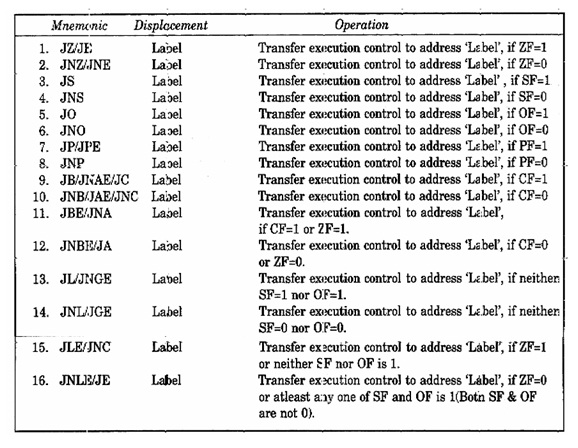
Last four instructions are utilized in the case of on signed binary number and decisions based operations, while all the remaining instructions may be utilized for unsigned binary operations. The terms below and above are usually utilized for unsigned numbers, while the terms greater and less are utilized for signed numbers. A conditional jump instruction that does not examine status flags for condition testing, is following:
JCXZ 'Label' Transfer execution control to address 'Label', if register CX is equal to zero.
The conditional LOOP instructions are shown in following table along with their meanings. These instructions can be used for implement structures like REPEAT_UNTIL, DO_WHILE etc.
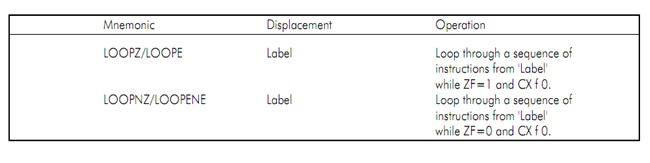
Figure: Conditional loop instructions
The ideas regarding all these instructions will be clearer with the programming practice. This topic is intended at introducing these instructions to the readers. Of course, the examples are quoted wherever possible but the LOOP and the JUMP instructions need a sequence of instructions for explanations and will be emphasized.