Collections:
The collection is an ordered group of elements, all of similar type (for illustration, the grades for a class of students). Each element has an exclusive subscript which determines its position in the collection. The PL/SQL offers 3 kinds of collections: the nested tables, index-by tables, and varrays . The Nested tables extend the functionality of the index-by tables (formerly known as the "PL/SQL tables").
The Collections works like the arrays found in mainly the third-generation programming languages. Though, collections can have only one dimension and should be indexed by integers. (In several languages like Ada and Pascal, arrays can have the multiple dimensions and can be indexed by inventory types.)
The Nested tables and varrays can store instances of an object type and, on the other hand, can be attributes of an object type. The collections can also be passed as the parameters. Therefore, you can use them to move the columns of data into and out of database tables or between the client-side applications and stored subprograms.
Syntax:
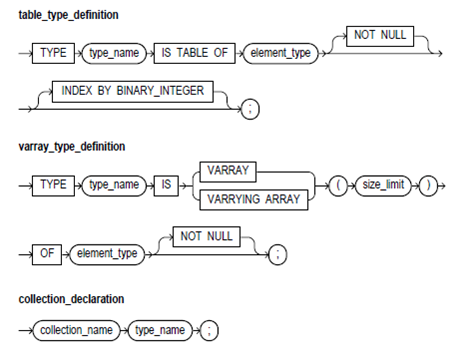
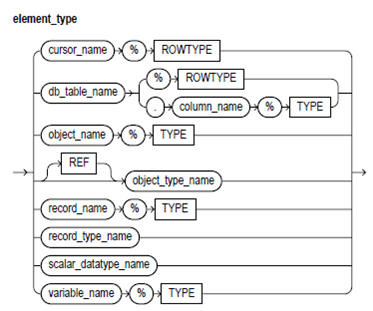
Keyword and Parameter Description
type_name:
These identify a user-defined type specifier that is used in the subsequent declarations of collections.
element_type:
This is any PL/SQL datatype except the BOOLEAN, BINARY_INTEGER, LONG, LONG RAW, NATURAL, NATURALN, NCLOB, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, object types with TABLE or VARRAY attributes, PLS_INTEGER, POSITIVE, SIGNTYPE, POSITIVEN, REF CURSOR, STRING, TABLE, or VARRAY. Also, with the varrays, the element_type cannot be CLOB, BLOB, or an object type with BLOB or CLOB attributes. If the element_type is a record type, every field in the record should be a scalar type or an object type.
INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER:
This optional clause defines the Version 2 PL/SQL tables that are called index-by tables in Version 8.
size_limit:
This is a positive integer literal which specifies the maximum size of a varray that is the maximum number of elements that the varray can contain.