Cohen Sutherland Line Clippings Algorithm
The clipping problem is identified by dividing the region surrounding the window area into four segments Up as U, Down as D, Left as L, Right as R and assignment of number 1 and 0 to respective segments assists in positioning the area surrounding the window. How this positioning of areas is performed can be well determined by understood in following figure.
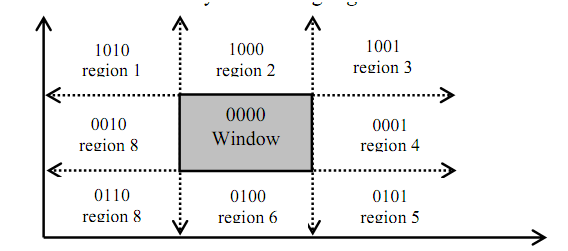
Figure: Positioning of regions surrounding the window
In figure as given above we have noticed that each coding of areas U, D, L and R is done along w.i.t. window region. Since window is neither Left nor Right, neither up nor down so, the respective bits UDLR are 0000; currently see area1 of above figure. The positioning code UDLR is 1010, that is the area1 lying on the position that is upper left side of the window. Hence, area1 has UDLR code 1010 i.e. Up so U=1, not Down so D=0, Left so L=1, not Right so R=0.
The sense of the UDLR code to identify the location of region w.i.t. window is:
1st bit ⇒ Up(U) ; 2nd bit ⇒ Down(D) ;3rd bit ⇒ Left(L) ; 4th bit ⇒ Right(R),
Currently, to perform Line clipping for different line segment that may reside within the window region partially or fully, or may not even lie in the widow area; we utilize the tool of logical ANDing among the UDLR codes of the points lying on the line.
|
Logical ANDing (^) operation
|
=>
|
1 ^ 1 = 1; 1 ^ 0 = 0;
|
|
between respective bits implies
Note:
|
|
0 ^ 1 = 0; 0 ^ 0 = 0
|
- UDLR code of window is 0000 all the time and with respect to this will generate bit codes of other areas.
- A line segment is observable if both the UDLR codes of the end points of the line segment equal to 0000 that is UDLR code of window area. If the resulting code is not 0000 then, which line segment or section of line segment may or may not be observable