Coordination number and geometry
Binary compounds are ones with two different elements present. 'Simple' crystal structures can be classed as ones in which each atom (or ion) is surrounded in a regular way by atoms (or ions) of the other kind. Even with this limited existence many structures are possible.
Although many are achieved with ionic compounds, some of these structures are shown by compounds with covalent bonding, and a discussion of the bonding factors involved in favoring one structure rather than another is deferred to
When the two elements B and A are not equivalent A is drawn smaller and with shading. In ionic compounds this is more general the metallic (cationic) element. If the role of cations and anions is reversed we speak of the anti-structure: thus Li2O has the, Cs2O the anti-CdI2 structure and anti-fluorite (CaF2) structure.
From the local point of view of each atom the most important characteristics of a structure are the coordination geometry and coordination number (CN). In the examples described these are the same for all atoms of the same type. Coordination numbers can be compatible with the stoichiometry. In AB both B and A have the same CN, the examples shown being
Zinc blende (4:4); Rocksalt (6:6); NiAs (6:6); CsCl (8:8).
When the stoichiometry is AB2 the CN of A has to be twice that of B:
Rutile (6:3); CdI2 (6:3); Fluorite (8:4).
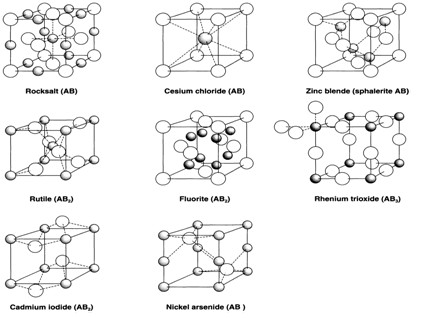
Fig. 1. A selection of binary structures.
In the structures illustrate many of the atoms have regular coordination geometry:
CN=2: linear (B in ReO3);
CN=3: planar (B in rutile);
CN=4: tetrahedral (A and B in zinc blende, B in fluorite);
CN=6: octahedral (A and B in rocksalt, A in NiAs, rutile and CdI2);
CN=8: cubic (A and B in CsCl, A in fluorite).