Laws of Radioactivity
All radionuclides do not decay at the same rate. From the kinetics point of view disintegration of any radionuclide is a first order process. There are two laws of radioactivity. As according to the first law of the radioactivity, the rate of disintegration of a radionuclide at any time is directly proportional to the number of atoms present at that time. Therefore,
- dN / λN = dt .........................(1)
where, N is the number of radioactive atoms of a specific radionuclide present at time t and λ is the nuclear decay constant (in s-1), a characteristic property of the radionuclide. The minus sign in Eq. (1) indicates that decay results in a decrease in number of atoms. The probability in which a radionuclide will disintegrate in a certain time interval does not depend on the state of chemical combination, the temperature, pressure or the presence of other atoms. At integrating Eq. (2), we get
N = N ºe -λt ................ (2)
where, No is the number of radioactive atoms present in the starting (at t = 0). It means that during the time interval t, (No - N) radioactive atoms would have undergone radioactive decay. Because Eq. (12.2) is exponential in nature and a plot of N vs. t (as shown in Figure) displays that radioactive decay never ceases or the number of radioactive atoms never becomes zero.
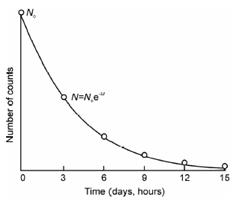
Figure: Decay plot of radioactive elements with time