Q: Find out the value of voltage Vo by using Norton's theorem .
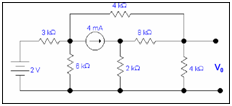
Sol:
We have to calculate V0 by using Norton's theorem.
Step 1: Replacing RL with a short circuit to search IN. Here RL is equal to 4k resistor.
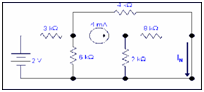
Step 2:
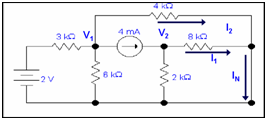
Isc =I1 + I2
Apply KVL for node 1
V1/4k + (V1 - 2)/3k + V1/6k +4m=0
3V1 +4V1 - 8 +2V1 +48 =0
9V1+40=0
V1= 4.44Volts
Now for node 2
V2/2k + V2/8k -4 =0
4V2 +V2 - 32 =0
5kV2 = 32
V2 =32/5 =6.4V
Now from the circuit we can say
I1 = V2/8k
= 6.4/8k
I1 = 0.8 mA
I2 = V1/4k
= 4.44/4k =1.11mA
Therefore,
IN = I1+ I2
IN = (1.11 + 0.8) = 1.91mA
Step 3: Determining RN
To compute RN we short circuit all of voltage sources and open the current sources.
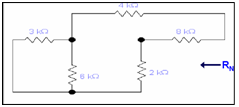
For RN
3k|| 6k = 2k
2k is in series through 4k = 2k + 4k= 6k
8k is in series with 2k = 8k + 2k=10k
10k ||6k = 10 x6/16
=60/16 =3.75k
Step 4:
After determining IN & RN, re-inserting the load resistance RL in the circuit in parallel RN and letting the IN current source parallel along these two resistances.
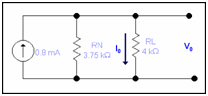
To find out V0
I0 = 1.91m x 3.75k x 1/(4k+3.75k) = 0.92mA
V0 = 4k x 0.92m=3.68 Volts