Life cycles in Amoebozoa
Amebae of the cellular slime molds (Dictyostelids) aggregate upon starvation to yield a multicellular pseudoplasmodium that differentiates into a fruiting body and generates haploid spores. Amebae of the acellular slime molds (Myxogastrids) fuse to form a diploid cell (or this is produced via haploid flagellated cells), which grows into a large multinucleate plasmodium. Sporangia arise and meiosis within them generates haploid spores that germinate to release amebae
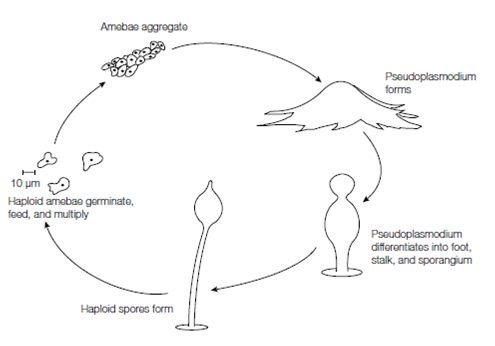
Figure: Life cycle of a cellular slime mold.
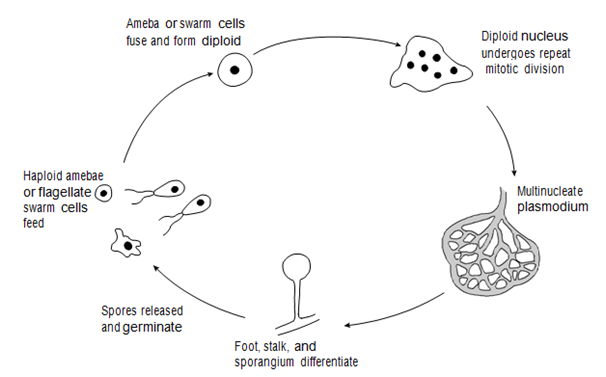
Figure: Life cycle of an acellular slime mold
Reproduction in the pathogenic amebae is by binary fission of the cell after mitotic division of the nucleus. A single cell splits to form two identical progeny. In the pathogenic species life cycles involve an encysted stage, which can resist adverse conditions in the environment. Once the cyst enters its target host tissue, external stimuli cause excystation and the production of amebic forms that colonize the host. On resumption of adverse conditions (i.e. leaving the host in excreta or other fluids), the amebae will encyst. Figure illustrates the life cycle of Acanthamoeba.

Figure: Life cycle of Acanthamoeba spp.