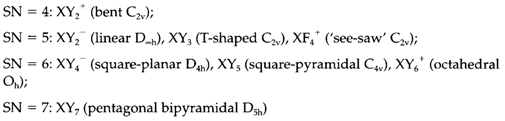Interhalogen and polyhalogen compounds
Binary compounds identified as interhalogen compounds with stoichiometry XYn are found among every pair of halogens F-I. N is an odd number for neutral molecules and when n>1 the terminal atom Y is all the time the lighter element. The greatest n found with a given pair increases with the variation in period number, some instances being IBr, BrF5, ICl3, and IF7. Most interhalogen compounds are obtained by direct reaction. They are very strongly oxidizing and the fluorides are fine fluorinating agents.
Several interhalogen and cations and polyhalogen anions are also known, some forming simply. For instance, aqueous solutions consisting of I- dissolve I2 to create I-3. In liquid BrF3 the following equilibrium take place:
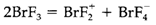
With the solvent-system concept In accordance, fluoride donors like NaF act as bases in this medium (providing Na+ and BrF4-), and fluoride acceptors like SbF5 act as acids (providing BrF2+and SbF6- ).
Another cationic species can be prepared through strong oxidation of the elements (example with AsF5) in a appropriate nonaqueous solvent. Instances include CI3+and Br2+ and I5+ that are also known in solid salts with anions like AsF6- .
Several species have the structures predicted through the VSEPR model. Listed as per the steric number (SN) below, the geometries and point groups are