Rankine Cycle
Whenever the system (i.e., the fluid being studied) alters its properties (i.e., pressure, temperature, and volume) from one value to other as a result of work or heat or internal energy swap, then it is said that the fluid has gone via a "process." In few procedures, the associations among pressure, temperature, & volume are identified as the fluid goes from one thermodynamic state to the other. The most general procedures are those in which the temperature, pressure, &volume is held constant throughout the process. These would be categorized as isobaric, isothermal, or isovolumetric processes, correspondingly. Iso means "stable or one." When the fluid passes via different procedures and then ultimately returns to the similar state it start with, and the system is said to have undergone a cyclic procedure. One such cyclic process employed is the Rankine cycle, two illustrations of which are shown in the figure below.
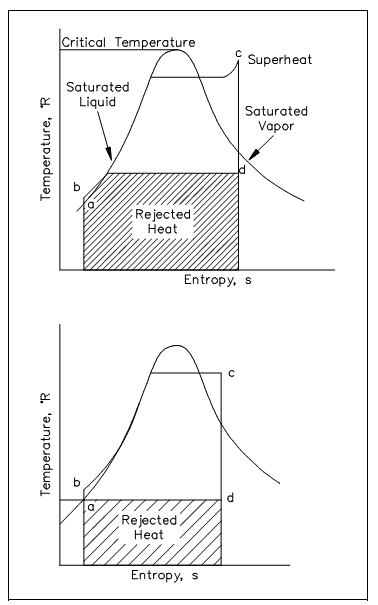
Figure: T-s Diagram with Rankine Cycles
The procedures which comprise the cycle are explained below.
ab: Liquid is dense with no change in entropy (i.e., by ideal pump).
bc: Constant pressure transfer of heat in the boiler. The heat is added to the compressed liquid, 2-phase, and superheat states.
cd: Constant entropy extension with shaft work output (i.e., in ideal turbine).
da: Constant pressure transfer of heat in the sink. Occupied heat is discarded to the heat sink (i.e., condenser).