The structure of the bacterial flagellum
Flagellin filament is only visible using the light microscope if it is complexed with another compound to increase its thickness. Filament is only 20 nm in diameter but can be up to 20 mm in length. In Gram-negative Bacteria the motor proteins are buried in the cytoplasmic membrane with a drive shaft passing by the peptidoglycan in the periplasm through the P ring and the outer membrane by the L ring. The drive shaft is attached to the flagellin filament through means of a flexible hook in Figure 1. The Flagella are biosynthesized from the MS ring upwards with motor P ring, L ring, proteins and the hook sequentially added. The hook has a cap on top and the flagellin filament elongates among these two substructures.
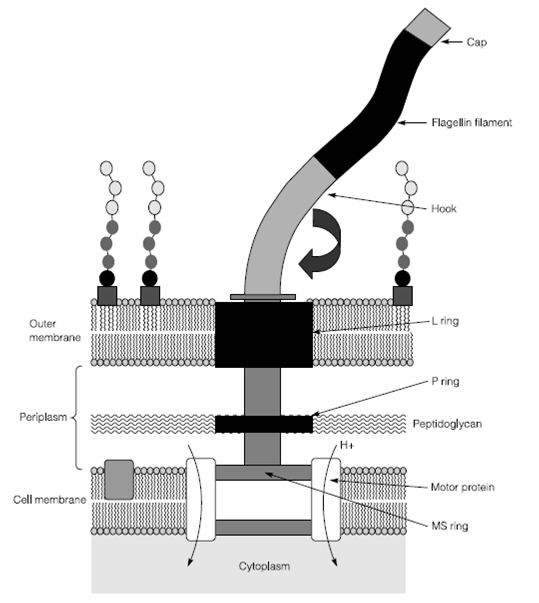
Figure 1: The Bacterial flagellum
The flagellar motor is an adapted proton uniport. The cell must have an electron potential gradient across the ingress and membrane of protons via the motor causes the MS ring and therefore the flagellin to rotate. This is an example of a simple bioenergetic process.