What is amino acids metabolism ?
Nitrogen enters the body through a variety of compounds present in the food, the most important being amino acids present in dietary proteins. The primary role of amino acids is in the synthesis of tissue proteins and other biosynthetic reactions. Amino acids contain nitrogen, which cannot be.stored, and therefore amino acids, which are in excess of biosynthetic needs of the cell, are degraded. This involves the following:
1. The removal of a-amino groups (amino groups attached to carbon atom next to the carboxyl carbon) by two processes called transmutation and oxidative deamination, forming ammonia and the corresponding a-keto acids, and
2. The conversion of ammonia to urea in the Urea Cycle. A portion of the free ammonia is excreted in urine, and the remaining is excreted in urine after getting converted to urea.
The carbon skeletons (structure left after the removal of amino group) of the a-keto acids are converted to common intermediates of energy producing metabolic pathways.
Lastly, the body has the capacity to produce certain specialized products from amino acids. A summary of nitrogen and amino acid metabolism is presented in Figure.
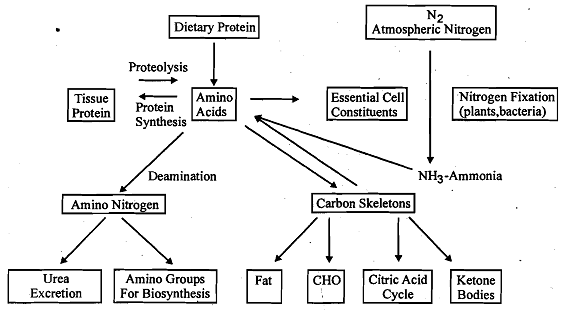
The amino acids that are released by the hydrolysis of dietary and tissue-protein, .mix Amino Acid and with other amino acids distributed throughout the body. This is called as amino acid Nucleclitidem etabolism pool. The amino acid pool contains LOO g of amino acid and is very small in compakon to .the amount of protein in the body. The concentration of free amino acids in the extracellular fluids is significantly lower than that within the cells of the body. The movement of amino acids from the extracellular space to the interior of the cells is by active transport mechanism which requires carrier molecule and energy from ATP, as you may recall reading.
The first step in the catabolism of all amino acids is the remval of a-amino group. Once removed, nitrogen can be incorporated into other compounds or excreted. We learnt earlier in this unit that the removal of the a-amino group can be achieved by the two processes, transamination and oxidative deamination. We shall get to know ' about these processes next.