In all previous illustrations, we assumed that coupon payments are paid on annual basis. However, most of the bonds carry interest payment semi-annually. Semi-annual coupon payments can be calculated by dividing the annual coupon payment and discount rate by 2. The time period n in the present value formula is treated in terms of 6-month period rather than years.
For example consider a 7%, 5-year bond with a discount rate of 6% and a maturity value of Rs.100. The cash flow, in the form of interest, for the first four and half years will be Rs.3.50 (Rs. 7/2) and last cash flow will be Rs.103.50, i.e., interest of Rs.3.50 and a principal of Rs.100.
The annual discount rate is 6% so semi-annual discount rate will be 3% (6% / 2).
When coupon rate is 7%, the semi-annual coupon rate is 3.5%. Then PV of cash flow will be:
Table 1: Calculation of PV of 7% Bond when Cash Flows are Semi-annual
|
Year
|
Cash Flow (in Rs.)
|
PV (in Rs.)
|
|
I half 2007
|
3.5
|
3.40
|
|
II half 2007
|
3.5
|
3.30
|
|
I half 2008
|
3.5
|
3.20
|
|
II half 2008
|
3.5
|
3.11
|
|
I half 2009
|
3.5
|
3.02
|
|
II half 2009
|
3.5
|
2.93
|
|
I half 2010
|
3.5
|
2.85
|
|
II half 2010
|
3.5
|
2.76
|
|
I half 2011
|
3.5
|
2.68
|
|
II half 2011
|
103.5
|
77.01
|
|
|
Present Value =
|
104.27
|
If we compare the PV of table 1 then we find that PV of table 1 is greater by Rs.0.06. This is because one-half the annual coupon payment is received six months sooner than when payments are annual.
We can divide the value of non-amortizing bond into two parts, first is PV of coupon payment and second is PV of maturity value. For fixed coupon rate, coupon payments represent an annuity. A short-cut formula for computing the value of bond when coupon rate is fixed and single discount rate is set for discounting the coupon payments, is to compute the PV of the annuity and then add the PV of maturity value. We can represent it in formula as follows:
V0 = 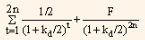
= I ¤ 2 (PVIFAkd ¤ 2,2n) + F(PVIFkd/2, 2n) ... Eq. (3)
Where,
V = value of the bond
I/2 = semi-annual interest payment
F = par value of the bond payable at maturity
kd/2 = required rate of return for the half-year period
2n = maturity period expressed in half-yearly periods.