The contents of compressed gas cylinders can range from highly flammable substances, such as hydrogen, propane and ethane (acetylene), to toxic gases, such as chlorine, sulphur dioxide, carbon monoxide etc., and to comparatively inert substances like argon, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen. The standard symbols used for the flammable and toxic gases. These gases can cause the following types of hazards in the event of a leakage.
Oxygen displacement: leading to asphyxiation of staff or laboratory animals.
Fire and explosion: oxygen or hydrogen enriched atmospheres can explode into fireballs moving with great force. Ignition can be by the slightest spark, e.g. from a light switch (spark free switches are available where this is a particular hazard).
Toxicity: gases may be toxic or even cause bums and irritation by skin contact.
These hazards can be minimised by following certain precautions, given below.
1) Ventilation; it is a good practice to ventilate a laboratory as soon as it is opened to disperse any accumulations of vapour, dust and gas. In any emergency, increased ventilation is essential; but beware of exposing others to risk in this way.
2) Respirators should be available where there is a real risk of gas hazards.
3) Where there is a risk of explosion due to gas, elimination of ignition sources is essential. This can be done by practising the following measures :
(a) use of spark-free electrical switches
(b) banning of all electric motors
(c) elimination of all sources of sparking from impact/friction
(d) a thorough warning sign system
(e) no experiments/work with flame
4) Large cylinders may weigh as much as 85 kg and should always be clamped vertically, Fig. 1 1.5, to prevent them toppling over or laid horizontally on the floor and fixed to prevent rolling. Damage could cause the base of valve stem, Fig. 1 1.6, to shear off and sudden release of pressure can propel a heavy gas cylinder across the room or through brick walls like a shell because compressed gas cylinders have gases stored under very high pressures.
5) The gas cylinders may be stored in open but should be protected from water, to avoid rusting and from extreme temperatures. These should not be heated beyond -50°C.
6) Care must be taken while moving cylinders, avoid dragging, rolling or sliding them. The use of a cylinder trolley is recommended.
7) The valve protection cap should not be removed if the gas is not to be used. Stiff cylinder valves must be opened carefully with hand pressure and not forced with hammers or wrenches with excessive leverage.
8) When the gas has to be passed through a liquid always use a check valve or a trap to prevent back suction of the liquid into the cylinder.
9) Always employ cylinders of suitable size so that the gas exhausts within a reasonable period of time.
10) Oil or grease must never be used on lines, releasing valves or other equipment for oxygen cylinders as this can cause explosions.
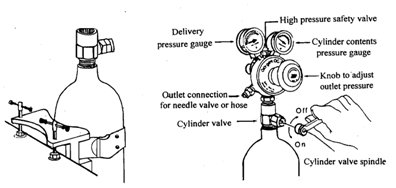
Figure: Valve and valve stem.
Despite the precautions taken there may be leakages and associated risks. Let us learn how to detect and manage a gas leakage.