Theories of Common Property Resource Management
The problems of commons arise due to the failure of the players to communicate and coordinate their actions. Let us present a simple example to highlight the situation of coordination failure. Suppose a CPR is exploited by two agents, agent A and agent B. They have to choose between two different techniques, X and Y, where X is inefficient compared to Y. The two techniques are interdependent in such a way that Y appears as a superior technique to an agent only if the other already uses it. Otherwise, X is chosen. By coordination failure, we mean the case where both the agents do not choose the superior technique Y because they fail to communicate and coordinate. They both reach to into an inferior Nash equilibrium, while Parep-dominating Nash equilibrium exists. Let us illustrate this with the payoff matrix given in below table. We consider the case of coordination between forest department and village community in managing a local forest.
Table: Pay-off Matrix for Local Forest
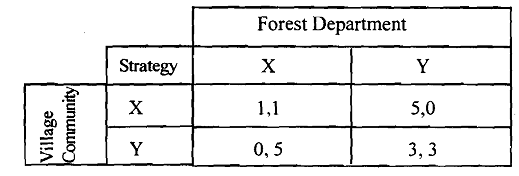
Both the players (forest department and village community) have two strategies: X and Y. Here X denotes 'do not participate or defect' and Y denotes 'participate or cooperate'. In the example of forest management, if the forest department and the village protection committee agree to participate, then the government and village committee may share the forest produce. The sharing rules can be such that the forest department collects revenue from timber sale, and the village community collects fodder and fuel. If the village committee decides not to cooperate or participate, it may indulge in cutting timber illegally and get its value or market price, and the forest department loses some income from timber sale. On the other hand, if the village community is to participate but not the forest department, then the forest department may collect all the forest produce, and auction it, but the village community will be the net loser. Finally, if both the forest department and the village community are not interested in participatory forest management, then the forest department may collect some timber and other forest produce, as well as fines and penalty from the people and the community may collect some forest produce by illegal methods. It is revealed from the above matrix that both the forest department and the village community may choose the inferior equilibrium (X, X), with a payoff (1, 1) and have no interest in a strategy such as (Y, Y) with. A payoff (3, 3). In the game structure given above, we cannot tell a priori whether equilibrium will be reached or not. What is interesting, however, is to consider that X is the old technique used since ages by both the agents, and Y is a new technique, which has just been made available. If the village community cooperates (opts for strategy Y) but the forest department does not (strategy X), then the entire benefit goes to the forest department. Similarly, if the forest department cooperates (opts for strategy Y) but the village community does not (opts for strategy X), then the entire benefit goes to the village community.
Theoretical arguments have been put forward to show that the tragedy of the commons, which inexorably leads to the destruction of the commons, is an unduly pessimistic story. An increasing number of scholars now advocate that collective action management by local people is, in most situations, the most appropriate strategy for managing CPRs.