THE CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU):
The CPU is the heart of any computing system. It executes the individual machine instructions, which make up a program. The CPU is formed from the following interconnected units:
1. ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit).
2. Registers.
3. Control Unit.
These units are shown as part of a computer system in Figure.
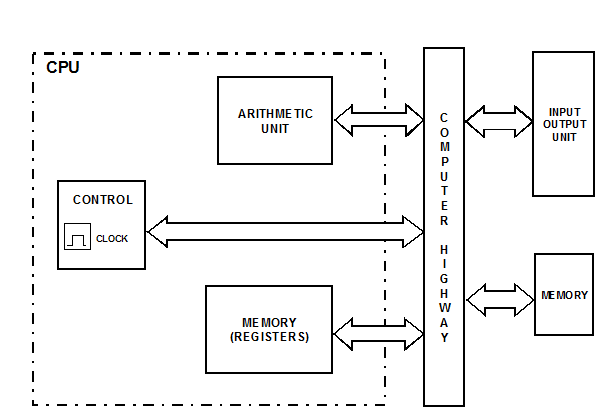
ALU. This is where the mathematics and logic functions are implemented.
It is not essential for the ALU to subtract, divide, or multiply, as these functions are easily achieved by using addition in conjunction with 2's complement arithmetic.
However, more powerful processors include sophisticated arithmetic hardware capable of division, multiplication, fixed and floating point arithmetic etc. Large processors also employ parallel operation for high speed.
Registers. These are temporary storage units within the CPU. Some registers have dedicated uses, such as the program counter register and the instruction register. Other registers may be used for storing either data or program information. Figure illustrates the principal registers within the CPU.
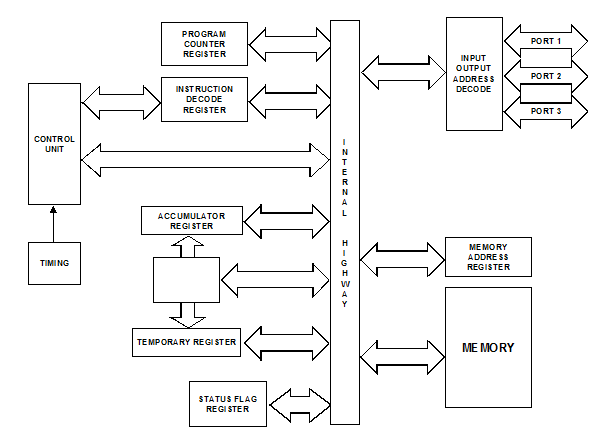
Program counter register. The instructions that comprise a program are stored in the computer's memory. Consequently, the computer must be able to sequentially access each instruction. The address of the first instruction is loaded into the program register, whereupon the instruction is fetched and loaded into another register, appropriately called the instruction decode register. Whilst the CPU is implementing the fetched instruction (e.g. Add, Shift, etc), the program counter register is incremented by 1 to indicate the address of the next instruction to be executed. This system, therefore, provides sequential execution of a program, provided that the program is written and stored sequentially in the memory.
The instruction decode register. As stated above, the program counter register locates the address at which the next instruction is to be found. The instruction itself is then transferred from memory into the instruction decode register. As the name implies, this register also incorporates a decoder. the output from the decoder places the necessary logic demands onto the ALU - i.e. shift, add, etc.
The accumulator register. This register is really part of the ALU, and it is the main register used for calculations. Consequently, it always stores one of the operands, which is to be operated on by the ALU. The other operand may be stored in any temporary register.
The status register. This register is a set of bistables which operate independently of each other. The bistables independently monitor the accumulator to detect such occurrences as a negative result of a calculation, a zero result, an overflow, etc. When such an occurrence arises, the output of the respective bistable is set (logic 1). It is then said to signal or flag the event. It is this register that gives a computer its decision-making capability. For example, if the result of a calculation in a navigational computer is zero, the program could instruct the autopilot to hold its present course. Alternatively, if the zero flag was not set, the computer would then decide to take corrective action.
There are many other registers within a CPU, some of which are general-purpose registers. These can be used to store operands or intermediate data within the CPU, thus eliminating the need to pass intermediate results back and forth between memory and accumulator.
The control unit. This unit is responsible for the overall action of the computer. It coordinates the units, so that events take place in the correct sequence and at the right time. Because it is responsible for timing operations it includes a clock (normally crystal controlled), so that instructions and data can be transferred between units under strict timing control (synchronous operation). The crystal and the clock generator may either be contained within the CPU, or supplied as separate components.