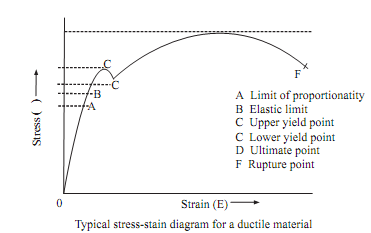
Stress-strain carves for ductile materials:
A material is said to be ductile in nature, if it elongates before fracture. One this type of material is mild steel. Shape of stress strain diagram for mild steel is shown in the figure given below.
A mild steel specimen of circular cross section or rectangular section is pulled until it breaks. The extensions of bar can be measured at every load increments. The stresses can be calculated based on the original cross sectional area and strains by dividing extensions by gauge length. When specimen of a mild steel is loaded in tension gradually, increasing tensile load, in the tension testing machine. The initial portion from O to A is linear where the strain linearly varies with stress. The line is called as line of proportionality and is known as proportionality limit. The stress corresponding to point is known as Limit of Proportionality. Hook's law obeys in this, slope of line gives, modulus of elasticity.
Further any increase in load increases extension rapidly and the stress strain diagram becomes curved. At the point B, material reaches elastic limit of it indicating end of elastic zone and entry into plastic zone. In most cases A and B coincide. If load is removed material returns to original dimensions of it.
Beyond elastic limit, the material enters into plastic zone and removal of load does not return specimen to its original dimensions, therefore subjecting the specimen to permanent deformation. On loading further the curve reaches the point 'C' called as upper yield point at which sudden extension occurs which is called as ductile extension where strain increases at constant stress. This can be identified by horizontal portion of the diagram. Point C gives yield stress beyond which load decreases with increase in strain up to C called as lower yield point.
After lower yield point has been crossed, stress again begins increasing, till stress reaches the maximum value at the point 'D'. The increase in load causes non linear extension up to point D. The point D called as ultimate point or maximum point. This point gives ultimate strength or maximum load of bar. The stress corresponding to highest point 'D' of stress strain diagram is called as ultimate stress.