Q. Show example on Ratio calculations?
The current gearing of Springbank plc = 100 × (3·5m/4m) = 87·5%
Total debt after issuing $3·4m of debt = 3·5m + 3·4m = $6·9m
New level of gearing = 100 × (6·9m/4m) = 172·5%
Current annual debenture interest = $350,000 (3·5m × 0·1)
Current interest on overdraft = 400,000 - 350,000 = $50,000
Annual interest on new debt = $272,000 (3·4m × 0·08)
Expected annual interest = 400,000 + 272,000 = $672,000
Current profit before interest and tax = $1·5m
Current interest cover = 3·75 (1·5m/0·4m)
Presume straight line depreciation additional depreciation = $600000 per year Expected profit before interest and tax = 1·5 + 1·43 - 0·6 = $2·33m
Expected interest cover = 3·47 (2·33/0·672)
This is lower than the current interest cover as well as assumes no change in overdraft interest. As a result Springbank's gearing is expected to rise from slightly below the sector average of 100% to significantly more than the sector average. Springbank's interest cover is probable to remain at a level lower than the sector average of four times and will be slightly reduced assuming no change in overdraft interest.
(ii) Ratio calculations
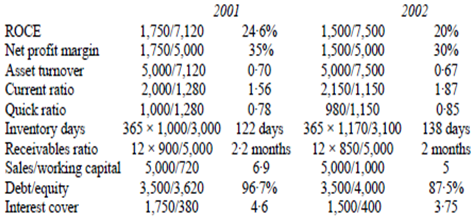
The return on capital employed of Springbank has decline as a result of both falling net profit margin and falling asset turnover while comparable with the sector average of 25% in 2001 it is well lower the sector average in 2002. The difficulty here is that turnover has remained static while both cost of sales and investment in assets have increased.
Despite the fall in prosperity both current ratio and quick ratio have improved in the main because of the increase in inventory levels and the decline in current liabilities the composition of which is unknown. The current ratio remains lower the sector average however. The raise in both inventory levels and inventory days together with the fact that inventory days is now 53% above the sector average may perhaps indicate that current products are becoming harder to sell a conclusion supported by the failure to increase turnover as well as the reduced profit margin. The expected rise in sales volume is therefore likely to be associated with a new product launch since it isn't likely that an increase in capacity alone will be able to generate increased sales. There is as well the possibility that the static sales of existing products may herald a decline in sales in the future.
The diminish in the receivables' ratio is an encouraging sign however the interpretation of the decreased sales/working capital ratio is uncertain. While the diminish could indicate less aggressive working capital management it could as well indicate that trade payables are less willing to extend credit to Springbank, or that inventory management is poor.
The gearing of the company has fallen but merely because reserves have been increased by retained profit. The interest cover has refused since interest has increased and operating profit has fallen. Given the steady long-term debt the increase in interest although small could indicate an increase in overdraft finance.
Ratio analysis tenders evidence that the financial performance of Springbank plc has been disappointing in terms of sales profitability and inventory management. It possibly that the management of Springbank see the increase in capacity as a cure for the company's declining performance.
(iii)
Ever since the investment has a positive NPV it is acceptable in financial terms. The threat highlighted by the analysis of recent financial performance is that existing sales may generate a declining contribution towards meeting interest payments in the future. Nevertheless sensitivity analysis illustrates the proposed expansion is robust in terms of sales volume since a 31% reduction in forecast sales is needed to eliminate the positive NPV. The proposed expansion is thus acceptable but the choice of financing is critical.
Springbank must be able to meet future interest payments if the cash flow forecasts for the increase in capacity are sound. But no account has been taken of expected inflation and both sales prices and costs will be expected to change. There is as well an underlying assumption of constant sales volumes when changing economic circumstances and the actions of competitors make this assumption not likely to be true. More detailed financial predicts are needed to give a clearer indication of whether Springbank is able to meet the additional interest payments arising from the new debentures. There is as well a danger that managers may focus more on the short-term require to meet the increased interest payments or on the longer-term need to replace the machinery and redeem the debentures rather than on increasing the wealth of shareholders.
Financial risk has risen from a statement of financial position point of view and this is likely to have a negative effect on how financial markets view the company. The cost of increasing additional finance is likely to rise while the increased financial risk may lead to downward pressure on the company's share price. The current debentures signify 54% of fixed assets and after the new issue of debentures this will rise to 73% of fixed assets. The assets available for contribution as security against new debt issues will therefore decrease and continue to decrease as fixed assets depreciate.
No information has been presented as to the maturity of the new debenture issue. If the identical principle is applied a medium term maturity of five to six years is indicated. Though the 10% debentures are due for redemption in 2007 and it would be unwise to have two significant redemption calls so close to each other.
On the base of the above discussion careful thought needs to be given to the maturity of any new issue of debentures and it perhaps advisable to use debt finance to meet only part of the financing need of the proposed capacity expansion. Substitute sources of finance such as equity and leasing should be considered.