Second degree price discrimination (two part-tariff)
An electric utility in Ontario has the following cost structure:
TC = 500 + 20Q
Suppose that the market (inverse of) demand for its electricity has been estimated to be
P(Q) = 100 - Q
where Q is the total quantity measured in kWh.
(a) Suppose that the price is set at marginal cost. What is the pro?t of the ?rm?
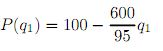
(b) Suppose that the price is set at average total cost. What is the price and output, and what is the dead weight loss? Compare deadweight loss in part (a) and (b)
(c) Suppose that each customer pays a connect ?xed fee charge to use the electric system and a usage price per each kWh. Assume that there 10 identical customers and the usage price per each kWh is set to marginal cost. What is the largest connect ?xed fee charge that each consumer would be willing to pay? What would be the deadweight loss?
Suppose that there are 6 class-1 customers with individual demand curves and 4 class-2 customers with individual demand curves
P(q2) = 100 - 80q2
Assume that the electric utility cannot charge a di?erent usage price per each kWh.
(d)What is the largest connect ?xed fee charge that a class-2 customer would be willing to pay as a function of P? What is the largest connect ?xed fee charge that a class-1 customer would be willing to pay as a function of P?
(e) Assume that the utility is serving to both class of customers. What is the optimal two part-tariff
( T = A + pq)? Find the value of A and q.
(f)What are the pro?ts of the electric utility under the optimal two part-tarff? What is the deadweight loss of the optimal two part-tariff?