In contrast to depth-buffer method, here we identify one surface at one time, scan-line method deals along with multiple surfaces. Since it processes each scan-line at one time, all polygons intersected from that scan-line are examined to find out that surfaces are visible. The visibility test includes the comparison of depths of all overlapping surfaces, to find out that one i.e. closer to the view plane. It is declared like a visible surface and the intensity values at the positions beside the scan- line are entered in the refresh-buffer, if it is determined.
Assumptions:
a) Plane of projection is Z=0 plane.
b) Orthographic parallel projection.
c) Direction of projection as: d = (0,0, -1)
d) Objects made up of polygon faces.
Scan-line algorithm resolves the hidden-surface issue, one scan-line at one time, generally processing scan lines starting the bottom to the top of the display.
The scan-line algorithm is a one-dimensional version of the Z-Buffer. We need two arrays, intensity [x] and depth [x] to hold values for a particular scan-line.
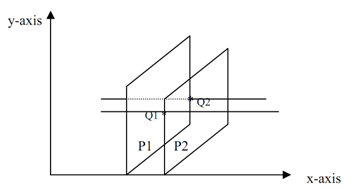
This time at Q1and Q2 both polygons are active that called sharing
Compare the z-values at Q1 for both the planes (P1 and P2). Let z1(1),z1(2) be the z-value at Q1 ,consequent to P1and P2 polygon correspondingly.
As the same z2(1), z2(2) be the z-value at Q2, consequent to P1and P2 polygon correspondingly.
Case1: z1(1)< z1(2)
z2(1) < z2(2)
In this case Q1, Q2 is filled along with the color of P2.
Case2: z1(2) < z1(1)
z2(2) < z2(1)
In this case Q1, Q2 is filled along with the color of P2.
Case3: Intersection is taking place.
In this condition we have to return to pixel by pixel and find out which plane is closer. After that choose the color of pixel