Pruning - Artificial intelligence
Remember that pruning a search space means deciding that particular branches should not be explored. If an agent surly knows that exploring a certain branch will not affect its selection for a particular move, then that branch may be pruned with no concern at all (for example : no effect on the outcome of the search for a move), and the speed up in search may be mean that additional depths may be searched.
When minimax approach is using either for an entire search tree or in a cut off search, there are often many branches which may be pruned because we find out speedy that the best value down a entire branch is not as good as the best value from a branch we have already explored. Such type of pruning is called alpha-beta pruning.
For an example, imagine that there are four choices for player one, called moves M1, M2, M3 and M4, and we are looking only 2 moves ahead (1 for player one and 1 for player two). If we do a depth first search for player one's move, we may work out the score they are guaranteed for M1 previous to even considering move M2. Imagine that it turns out that player 1 is guaranteed to score 10 with move M1. We may use this information to reject move M2 without checking all the possibilities for player two's move. For example, suppose that the first option possible for player 2 after M2 from player one means that player 1 will score overall 5 only. We know, In this case, that the maximum player one can score with M2 is 5 or less. Player one, Of course won't select this, because M1 will score 10 for them. We see that there is no point checking all other possibilities for M2. This can be seen in the following diagram (ignore the X's and N's for the time being)
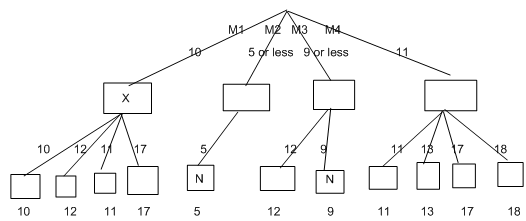
We see that we could reject M2 straight away ,thus in the search space save ourselves 3 nodes. We could reject M3 after we came across the 9, and in the end of the game M4 turns out to be better than M1 for player one. Totally , by using alpha-beta pruning, we avoided looking at 5 end nodes out of 16 - around 30%. If the calculation to assess the scores at end-game states (or estimate them with an evaluation function) is computationally expensive, then this saving could enable a much high search. Moreover, this kind of pruning can arise anywhere on the tree. The general principles are that:
1. Given a node N which can be selected by player 1, then if along any path, there is another node X, such that (a) X can be selected by player two (b) X is on a higher level than N and (c) X has been shown to guarantee a bad score for player 1 than N, then all the nodes with the same parent as N may be pruned.
2. Given a node N that can be selected by player two, then if there is a node X along any path such that (a) player one can select X (b) X is on a greater level than N and (c) X has been shown to guarantee a better score for player one than N, then all the nodes contain same parent as N can be pruned.
For an exercise: which of the principles from these did we use in the M1 - M4 pruning example above? (To make it easy, I've written on the N's and X's).
Because we may prune using the alpha-beta method, it makes sense to carry out a depth-first search using the minimax principle. In the Comparison to a breadth first search, a depth first search will get to aim states quicker, and this information may be used to determine the scores guaranteed for a player at specific board states, which in turn used to perform alpha-beta pruning. If a game-playing agent used a breadth first search instead of then only right at the end of the search would it reach the goal states and begin to perform minimax calculations. Hence, the agent would miss much potential to peform pruning.
By using a depth first search and alpha-beta pruning is quite sensitive to the order in which we try operators in our search. For an example in above, if we had selected to look at move M4 first, then we would have been able to do more pruning because of the higher minimum value (11) from that branch. Often, it is worth to spending some time in working out how best to order a set of operators, as this will highly increase the amount of pruning that may occur.
It is clear that a depth-first minimax search with alpha-beta pruning search dominates minimax search alone. In fact if the effective branching rate of a general minima search was b, then by using alpha-beta pruning will reduce this rate to b. This means, In chess, that the effective branching rate reduces from 35 to around 6, meaning that alpha-beta search can look further moves ahead than a normal minimax search with cutoff.