A gas is a fluid. It has no resistance to change of shape and will expand indefinitely to fill any container in which is held. The molecules or atoms which make up a gas interact only weakly with each another. They move rapidly, and collide randomly and chaotically with one another. The physical properties of a perfect gas are completely described by four parameters which, with their respective SI units are:
?The amount of substance of which it is comprised, n, in moles;
?The temperature of the gas, T, in Kelvin;
?The pressure of the gas, p, in Pascal;
?The volume occupied by the gas ,V, in m3.
The perfect gas equations
Several separate gas laws were independently developed:
Boyle's law: p.V=constant (at constant temperature)
Charles' law: 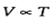 (at constant pressure)
(at constant pressure)
Avogadro's principle: 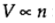 (at constant pressure and temperature)
(at constant pressure and temperature)
These three laws are combined in the perfect gas equation of state (also known as the ideal gas law or the perfect gas equation)
The perfect gas equation
pV=nRT
The four parameters of perfect gas are not independent and the relations between parameters are expressed in the gas laws. The perfect gas laws are unified into a single equation of state for a gas which fully expresses the relationships between all four properties. These relationships, however, are based on approximations to experimental observations and only apply to a perfect gas.
Partial pressure:
The pressure of a mixture of gases in a particular volume is the sum of the partial pressure of each individual constituent gas, with the partial pressure of each gas being the pressure that it would exert if it alone occupied the same volume. Dalton's law is strictly true only for ideal gases
The total pressure exerted by a mixture of ideal gases is related to the partial pressures through Dalton's law, which may be illustrating as:
"The total pressure exerted by a mixture of ideal gases in a volume is equal to the arithmetic sum of the partial pressures".
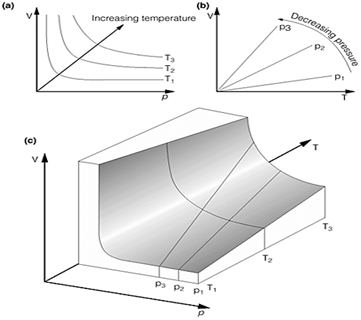
Fig.1. Graphical representations of the ideal gas equations. (a) Boyle's law; (b) Charles' law;(c) The surface